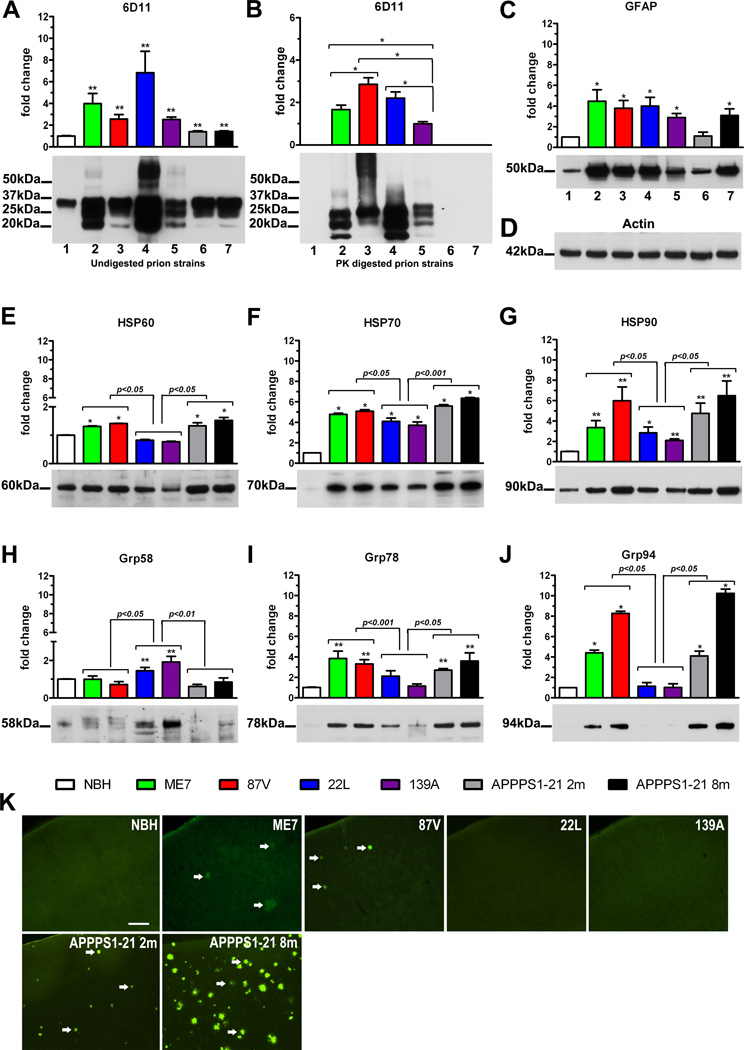
Figure 1.
Biochemical and histological analysis of brains from NBH-inoculated control mice; mice inoculated with ME7, 87V, 139A, and 22L prion strains; and two (2m) and eight (8m) months old APPPS1-21 AD Tg mice. Biochemistry: densitometric analysis (n=6 per group) and representative Western immunoblots profiling the steady-state levels of total PrP (A), PrPSc (B); GFAP (C), actin (D, used as the loading control), HSP60 (E); HSP70 (F); HSP90 (G); Grp58 (H); Grp78 (I), and Grp94 (J). Values in the graphs show the mean fold change of band intensities (±SEM) analyzed by densitometry relative to those in the control NBH-inoculated animals, except for (C) which shows the mean fold change of band intensities relative to those in 139A infected animals. The average band density in the control NBH-inoculated animals used as a reference value was calculated for each protein separately. Asterisks above the bars denote results of pair-wise comparison against the control NBH-inoculated mice: * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Results of comparison between pairs of amyloidogenic ME7 and 87V prion strains, APPPS1-21 mice and non-amyloidogenic 139A and 22L prion strains are shown directly above the brackets spanning the groups. The position of protein size markers next to Western immunoblots are indicated in thousand of Daltons (kDa). Histology: (K) representative images of coronal sections through S1 cortical area stained with Thioflavin-S. Arrows indentify Thioflavin-S binding amyloid plaques. Scale bar =100µm.