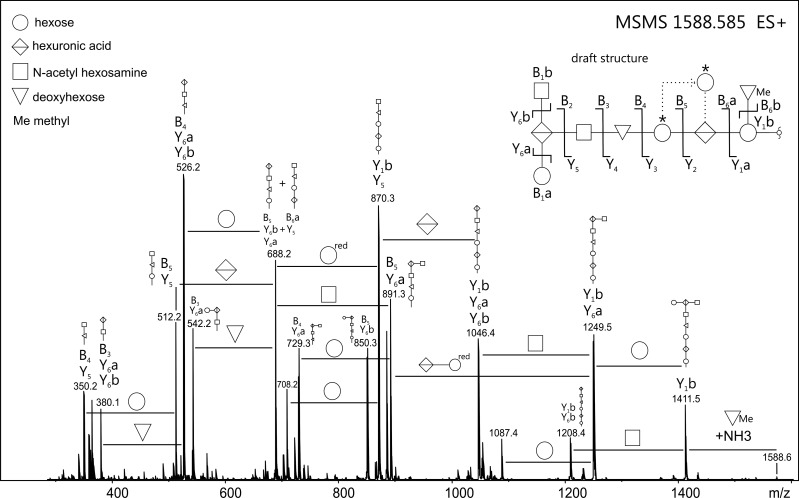
Fig. 3.
ESI-TOF-MS/MS spectrum of the borohydride-reduced B. fragilis O-glycan, as observed from protein bands excised from SDS–PAGE gels. The fragmentation pattern revealed the presence of a nine-sugar oligosaccharide comprising three hexoses, two hexuronic acids, two N-acetyl hexosamines as well as two deoxyhexoses (modified or free). Based on the observed fragment ions, the B. fragilis O-glycan structure was drafted (see inset top right). Fragments were labeled using the nomenclature as described (Domon and Costello 1988). The terminal N-acetyl hexosamine residue is found with considerable uncertainty, both by its accurate mass (see Supplementary data, Table S1) and the fact that it is prone to loss of a 42 Da fragment (indicating O-acetylation rather than N-acetylation) during β-elimination. In addition, the existence of a glycan isoform with the middle of the three hexose residues (marked with asterisk) branching from the hexuronic acid residue cannot be completely ruled out. Potential rearrangement artifacts upon CID were excluded upon measurement of sodium adducts of the B. fragilis O-glycan (Wuhrer et al. 2011; data not shown). Note: Line positions between residues of the draft B. fragilis O-glycan structure do not represent actual linkage types.