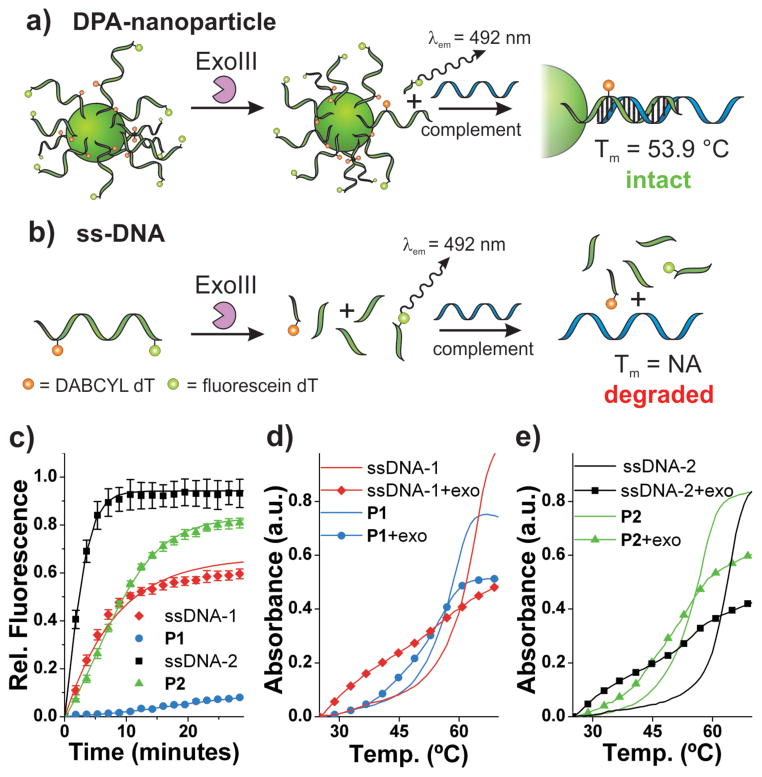
Figure 3.
Exonuclease resistance of DPA nanoparticles. a) Scheme depicting DPA-nanoparticle resistance to Exonuclease III and consequently, intact DNA at the particle surface available for hybridization with complementary ssDNA. b) Scheme depicting ssDNA being degraded by ExoIII and consequently, no intact DNA available for hybridization with complementary ssDNA. c) Exonuclease III activity over time monitored by fluorescein fluorescence dequenching (λex = 485 nm, λem = 535 nm). d) Thermal denaturation analysis with and without Exo III treatment for P1 and ssDNA-1. λabs = 260 nm. Samples subjected to enzyme for 60 minutes at 37 °C. P1 + Complement: Tm = 58.8 °C; P1 + Exo III + Complement: Tm = 55.8 °C). e) Thermal denaturation analysis with and without Exo III treatment for P2 and ssDNA-2. λabs = 260 nm. Samples subjected to enzyme for 60 minutes at 37 °C. P2 + Complement: Tm = 56.9 °C; P2 + Exo III + Complement: Tm = 53.9 °C). See Supporting Information Figure S13 for derivative plots of melting temperatures. Complement: 5′-TATTATATCTTTAGACAC TGACTGGACATGACTCT-3′