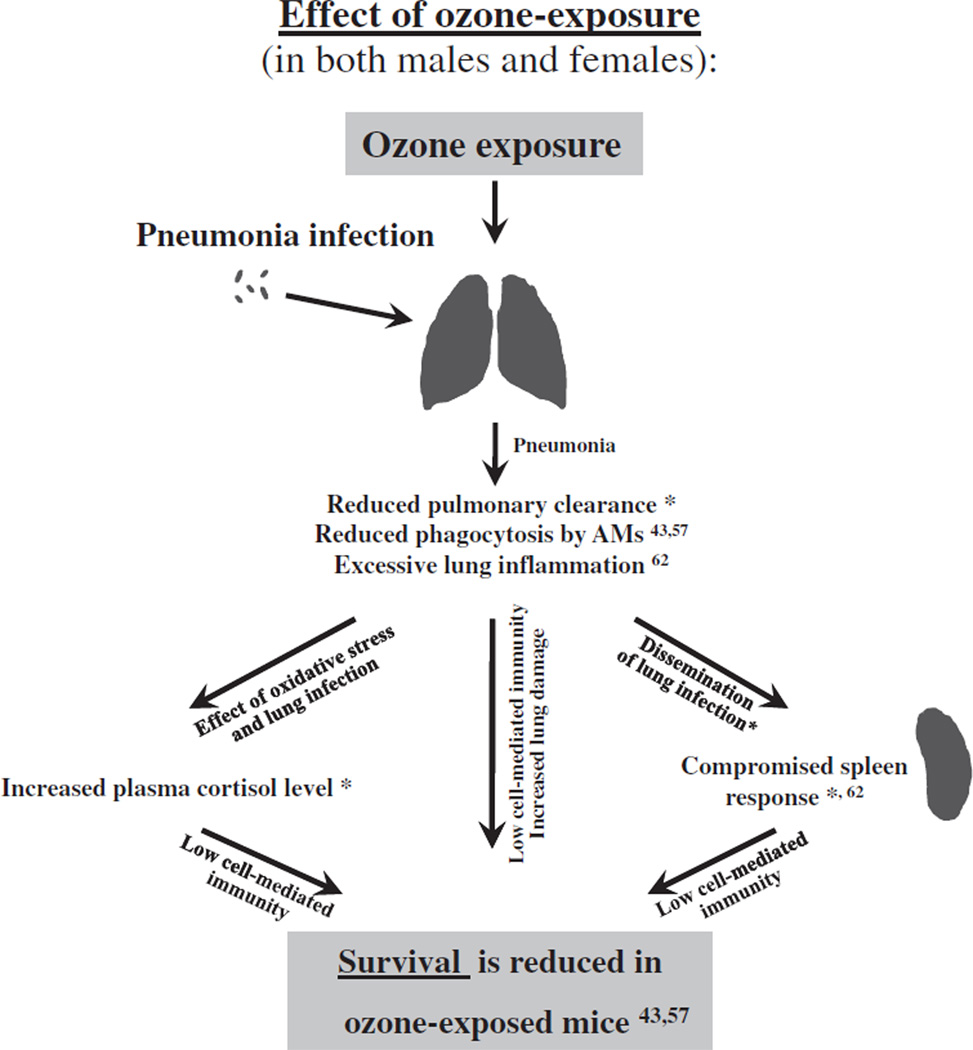
Fig. 6.
Overview of the effect of ozone exposure on the outcome of pneumonia. The effect of ozone exposure on mouse survival after pneumonia is depicted diagrammatically. We have observed previously that ozone-exposed male and female mice exhibited lower survival than FA-exposed mice after pneumonia [43,57]. A summary of the findings from the present study and the literature where this mouse model has been used is provided to indicate factors or processes that may explain and/or contribute to the previously observed differential survival in response to ozone exposure. Reduced pulmonary clearance (this study*), reduced level of in vivo phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages [43,57], excessive lung inflammation [62], a compromised spleen response to infection (this study*, and [62]), and increased plasma stress hormone cortisol level (this study*) may account for the survival difference between ozone- and FA-exposed animals (males or females: ozone < FA) [43,57].