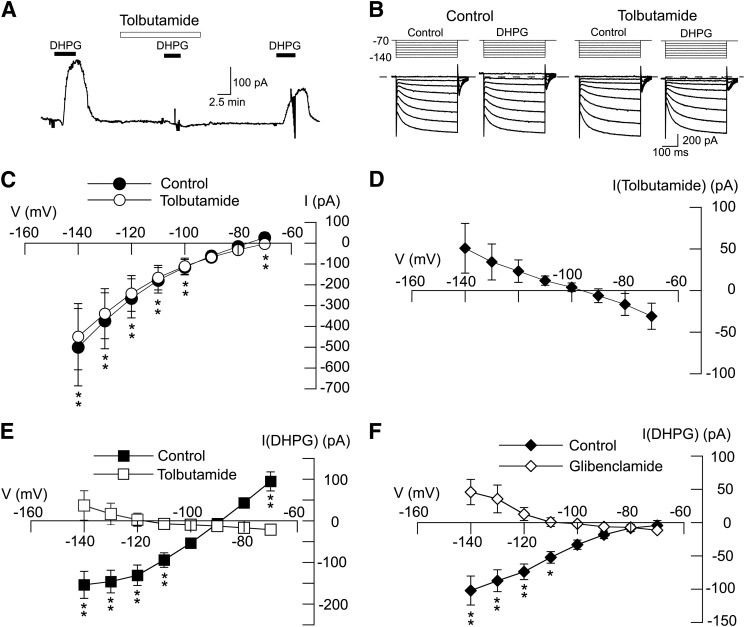
Fig. 2.
DHPG-evokes sulfonylurea-sensitive currents in STN neurons. (A) Current trace shows that tolbutamide (100 μM) blocks DHPG-evoked outward current (at −70 mV). Note that DHPG caused a small inward current in the presence of tolbutamide. (B) Current traces recorded during a series of hyperpolarizing voltage steps (from −70 to −140 mV) show that the DHPG-evoked conductance increase is prevented by tolbutamide (100 μM). (C) I-V plots showing whole-cell conductance before (control) and during superfusion with 100 µM tolbutamide (n = 6). (D) I-V plot showing net (subtracted) currents evoked by tolbutamide; I-V plot was derived from data shown in (C). (E) I-V plots show that tolbutamide (100 μM) significantly altered the voltage-dependence of currents evoked by DHPG (n = 11; P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with RM). Note that tolbutamide changed the slope conductance of DHPG-evoked currents from positive to negative. (F) I-V plots show that glibenclamide (1 μM) significantly altered voltage-dependence of currents evoked by DHPG (n = 6; P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with RM). Significant differences at specific test potentials: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Holm-Sidak tests.