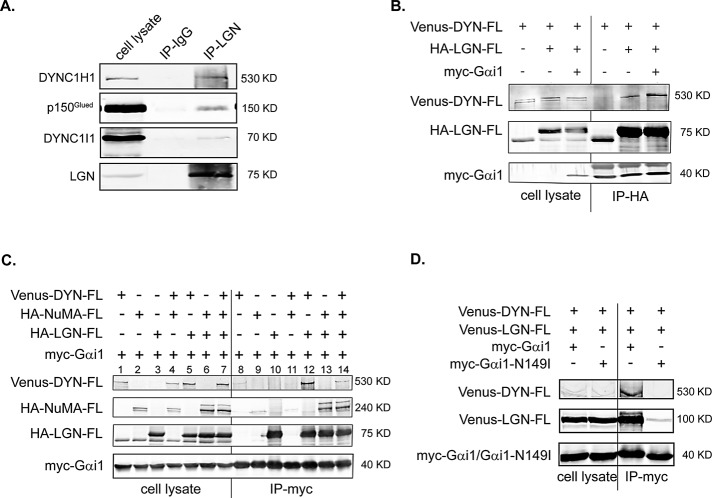
FIGURE 1:
Gαi-regulated interaction between LGN and DYNC1H1. (A) Endogenous LGN and cytoplasmic dynein form a complex. MDCK II cells were partially synchronized by treating with nocodazole (200 nM) for 12 h. After being released from the treatment for 40 min, cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-LGN antibodies or rabbit IgG. The immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS–PAGE and blotted using specific antibodies. (B) Gαi enhances the association between LGN and DYNC1H1. Cos 7 cells were transfected as indicated. Cell lysates (1/30 of total) and immunoprecipitates were separated in a 6% SDS–PAGE gel and blotted using specific antibodies. Note that in 6% gel, myc-Gαi1 comigrated with and was masked by the light chain of anti-HA antibody in the HA-LGN immunoprecipitates. (C) Gαi, LGN, and DYNC1H1 form a complex in vivo, independent of NuMA. Cos 7 cells were transfected as indicated. Cell lysates (1/30 of total) and immunoprecipitates were separated in a 7% SDS–PAGE gel and blotted. (D) The GoLoco-insensitive Gαi1 cannot associate with LGN and DYNC1H1. Cos 7 cells were transfected as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to analysis as in C.