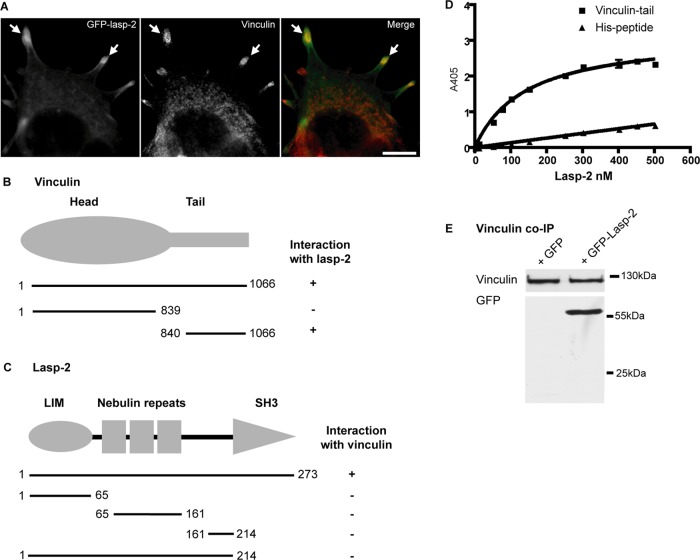
FIGURE 2:
Lasp-2 interacts with vinculin. (A) Lasp-2 (green) colocalizes with vinculin (red) at focal adhesions. HEK 293 cells were transfected with GFP–lasp-2 and stained for vinculin. Areas of colocalization are highlighted with arrows. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) For analysis with the yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) system, yeast strain AH109 was cotransfected with a bait coding for lasp-2 and a prey coding for vinculin. Various vinculin prey fragments were then cotransformed with lasp-2, and the binding site for lasp-2 on vinculin was determined to be within the vinculin-tail. (C) Also using the Y2H system, the binding site for vinculin on lasp-2 was found to be the SH3 domain of lasp-2 using different lasp-2 bait constructs. (D) Lasp-2 binds to vinculin-tail in a saturable manner in ELISA. A 10-pmol amount of vinculin-tail or His-peptide (negative control) was immobilized on microtiter plates and incubated with increasing amounts of lasp-2. Bound lasp-2 was detected with an anti–lasp-2 antibody. Lasp-2 bound to vinculin-tail but much less to His-peptide. (E) Lasp-2 coimmunoprecipitates with vinculin. Endogenous vinculin was immunoprecipitated from HEK 293 cell lysates expressing either GFP or GFP–lasp-2. GFP–lasp-2 coimmunoprecipitated with vinculin.