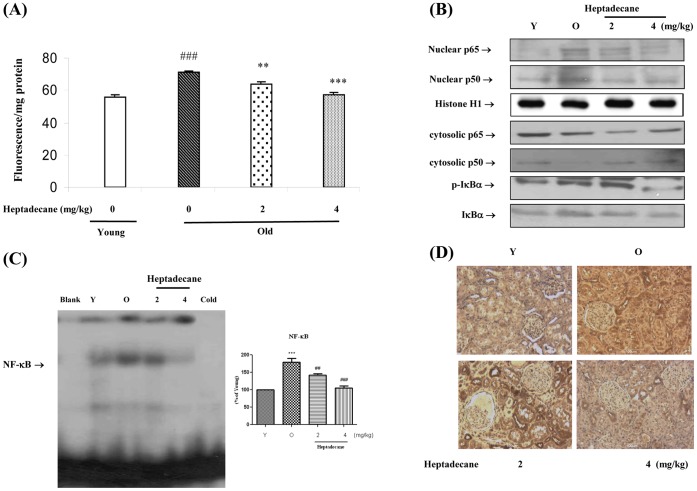
Figure 1. Heptadecane suppressed age-related increases in NF-kB activity.
(A) RS generation in aged rat was determined by observing the effects of age and heptadecane using the DCFHDA method and kidney homogenates. The values shown are means ± SEs for 5 rats. Young = 9-month-old baicalin untreated rats; Aged = 20-month-old, heptadecane untreated rats. Values are means ± SEs for 5 rats. ###p<0.001 vs. Young rats; **p<0.01 vs. age-matched rats; ***p<0.001 vs. age-matched rats by one factor ANOVA. Western blot was performed to detect (B) nuclear p50 and p65 protein levels in nuclear extracts (30 µg protein) and age-related IkBα, IkBβ, and IkBα phosphorylation degradations in cytoplasmic extracts (40 µg protein) in young, aged, and aged rats fed heptadecane. (C) EMSA method was used to compare the nuclear NF-kB binding activities of aged rat fed heptadecane and aged counterparts. One representative result of three experiments that yielded similar results is shown. Young rats (9 months of age) and aged (20 months of age) were utilized. Heptadecane was fed to the aged rat at 2 mg or 4 mg/Kg per day for 10 days. Statistical significance: results of one-factor ANOVA: ***p<0.001 vs. young rat; ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 vs. old non-heptadecane-fed rats, respectively. (D) Immunoreactivity was determined by NF-kB (p65) in renal tissue of age and heptadecane (Immunohistochemistry, ×100).