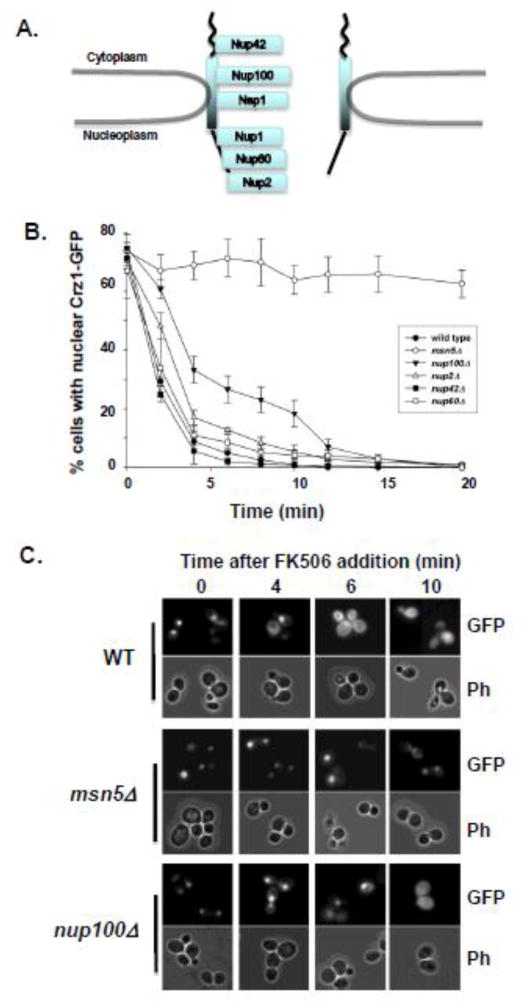
Figure 2.
Crz1-GFP is exported from the nucleus at different rates in different nup mutants. (A) Schematic cartoon of the location within the NPC of Nups investigated using the in vivo nuclear export kinetics assay. (B) Yeast cells expressing Crz1-GFP were examined for Crz1 export kinetics after addition of FK506 as described in figure 1 and Materials and Methods. Wild type cells (-●-) and mutants lacking Msn5 (msn5Δ -○-), Nup100 (nup100Δ -▼-), Nup2 (nup2Δ -△-), Nup42 (nup42Δ -■-), and Nup60 (nup60Δ -□-) were assayed. Data points represent mean percentage of cells with nuclear Crz1-GFP and error bars represent standard error of the mean. (C) Direct fluorescence microscopy was performed on wild type (WT), msn5Δ, and nup100Δ cells expressing Crz1-GFP. Cells were treated with Ca2+ and photomicrographs were taken prior to FK506 addition (0), and at 4, 6, and 10 minutes after the introduction of FK506.