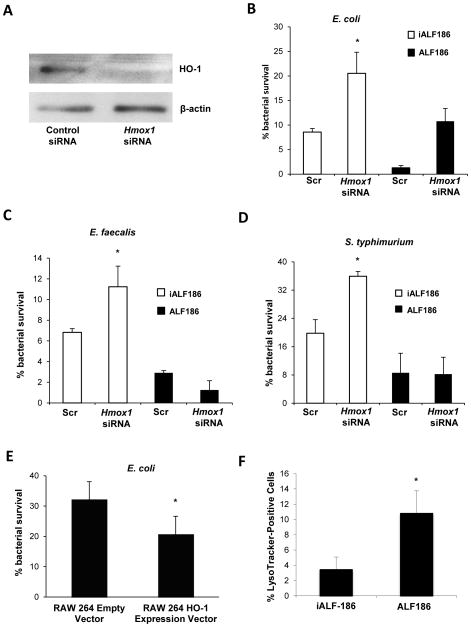
Figure 6. HO-1 and CO enhance macrophage bactericidal activity.
(A) siRNA was used to knock down Hmox1 in WT BMDMs. Total protein was isolated and analyzed for HO-1 expression by Western blot to assess gene silencing. BMDMs were analyzed for macrophage bactericidal activity against (B) E. coli (C) E. faecalis and (D) S. typhimurium using gentamicin protection assay. siRNA transfected cells were also cultured in the presence of ALF186 (black bars) or inactive iALF186 (white bars) to study the effect of CO on bactericidal activity. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (E) RAW 264.7 macrophages that stably overexpress Hmox1 were used in gentamicin protection assays against E. coli K12. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments, *p < .05 vs. scrambled siRNA transfected BMDMs. (F–G) BMDMs were incubated with ALF186, iALF186 (100 μM), CoPP (10 μM) or DMSO, then cells were treated with LysoTracker® (100 nM), and exposed to K12 E. coli. Cells were then fixed and nuclei stained with Topro-3, 5 nM. LysoTracker® positive cells were calculated as a percentage of total cells. At least 10 high powered fields and at least 100 cells were counted. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *p < .05.