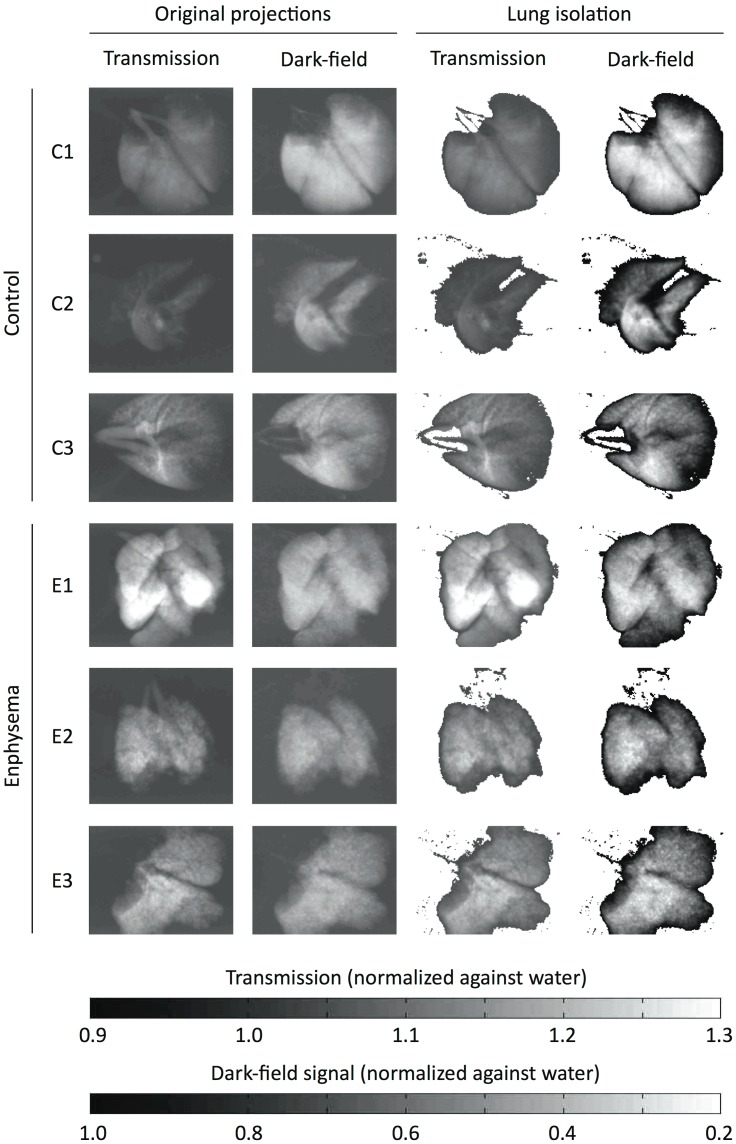
Figure 1. Original and segmented transmission and dark-field projection images.
On the left, the transmission and dark-field signal from one original projection image is shown for each control (C1-3) and emphysema (E1-3) mouse. Out of 11 projections acquired for each lung, one sample projection was chosen visually such as to display both lungs with the least possible overlap (thus resembling a frontal chest radiograph). Lung tissue areas were isolated from the images using a dark-field signal threshold for segmentation. The threshold was visually determined as the border of background noise and the signal peak on dark-field signal histograms. This segmentation was used for both dark-field and transmission images, such that identical lung areas were isolated on both images. The resulting isolated images are shown on the right. Note that this segmentation approach validly distinguishes pulmonary parenchyma from background signal and also removes most of the trachea and main bronchi.