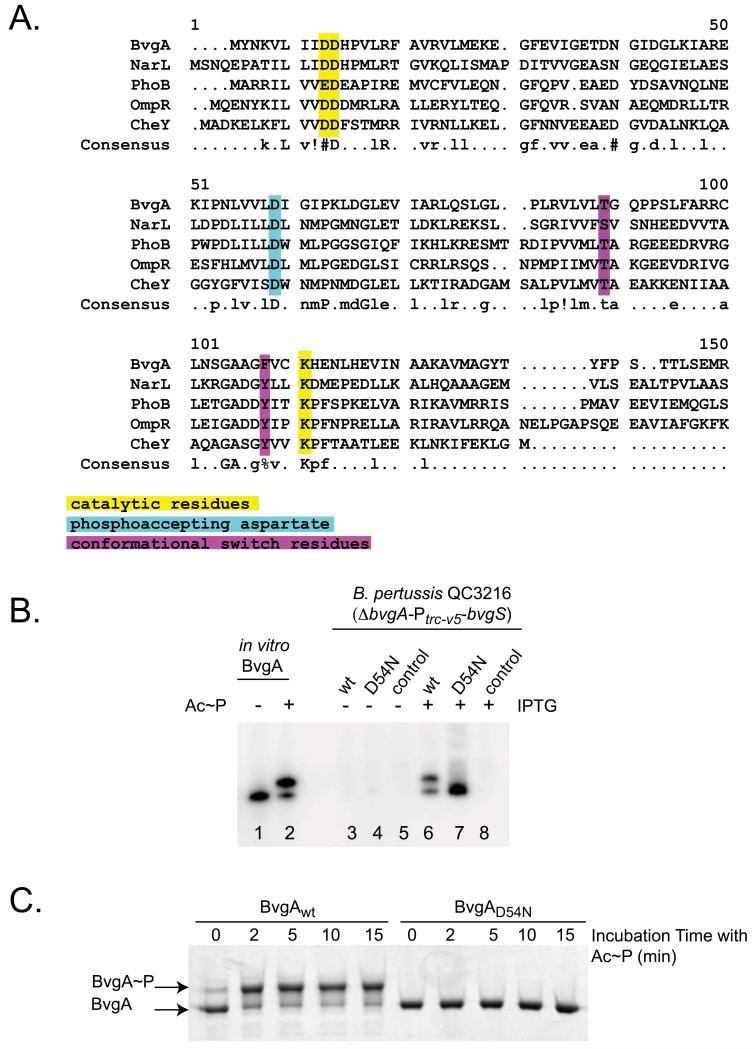
Figure 4. Mutation of the aspartic residue at position 54 eliminates BvgA phosphorylation in B. pertussis.
A. Alignment of different response regulator protein sequences using the Multalin web program. (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/). The parameters used correspond to the default parameters of the program. Consensus symbols are:! for L, M; % for F, Y; and # for N, D, Q, E, B, Z. Catalytic residues are highlighted in yellow, the phosphoaccepting aspartate in teal, and conformational switch residues in purple, with reference to Dyer & Dahlquist (2006) and Ruiz et al. (2008).
B. BvgAD54N is not phosphorylated in B. pertussis. Strains of B. pertussis strain QC3216 (ΔbvgA-Ptrc-v5-bvgS) harboring plasmids directing the synthesis of wild-type BvgA (pSS4983, lanes 3 and 6), BvgAD54N (pSS5027, lanes 4 and 7), or the empty pQC1883 vector control (lanes 5 and 8) were analyzed for BvgA synthesis and phosphorylation without (lanes 3-5) and with (lanes 6-8) IPTG-induction. Control lanes contained 1 pmol of purified BvgA (lane 1) or BvgA~P, (lane 2)
C. Kinetics of in vitro phosphorylation of wild-type BvgA and BvgAD54N. Purified wild-type BvgA and BvgAD54N (25 pmol each) were phosphorylated by treatment with Ac~P for the indicated amount of time prior to sample preparation and Phos-Tag™ gel electrophoresis. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie staining.