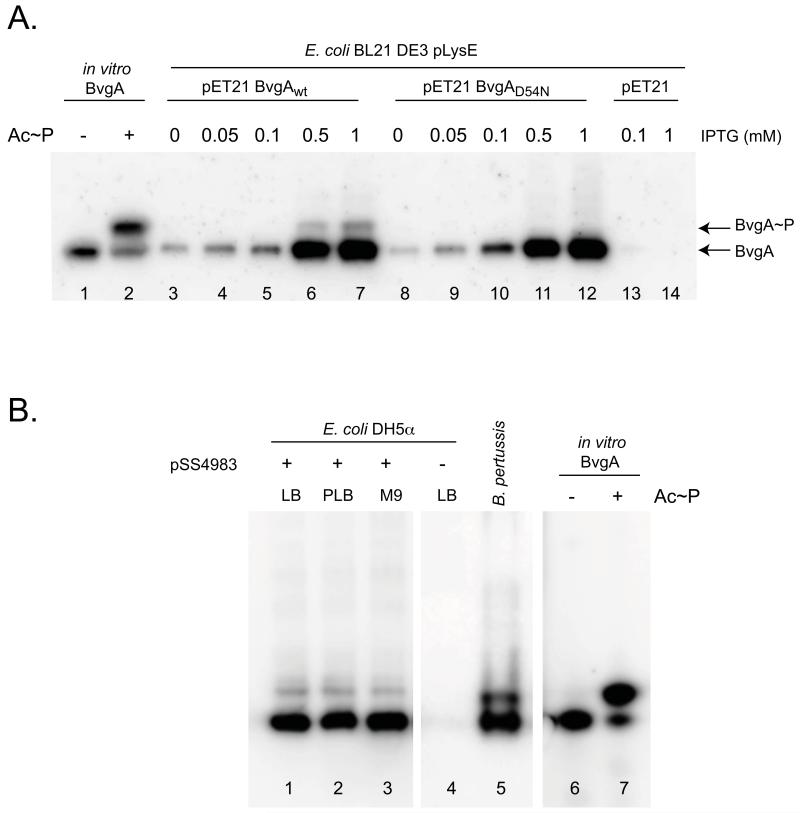
Figure 6. BvgA is phosphorylated in E. coli in the absence of BvgS.
A. Phosphorylation of BvgA in E. coli is dependent on D54. Cultures of E. coli BL21(DE3)/pLysE cells containing pET21a(+) alone (lanes 13-14), or pET21a(+) expressing wild-type bvgA (lanes 3-7) or bvgAD54N (lanes 8-12) were incubated for one hour with increasing concentrations of IPTG and analyzed by Phos-tag™ gel electrophoresis and Western blot as described above. Control lanes contained 1 pmol of purified BvgA (lane 1) or BvgA~P (lane 2).
B. Effect of growth medium on BvgS-independent phosphorylation of BvgA in E. coli. Cell lysates of E. coli DH5α with (lanes 1-3) or without (lane 4) pSS4983 (expressing wild-type BvgA under IPTG induction) were assessed for phosphorylation of BvgA in vivo after growth for three hours in LB (lanes 1 and 4), PLB (lane 2), or M9-glucose (lane 3) media, each supplemented with 2 mM IPTG. A B. pertussis culture (lane 5), purified BvgA (lane 6), and in vitro phosphorylated BvgA (lane 7) are shown for comparison.