Figure 1.
Autophagosome formation
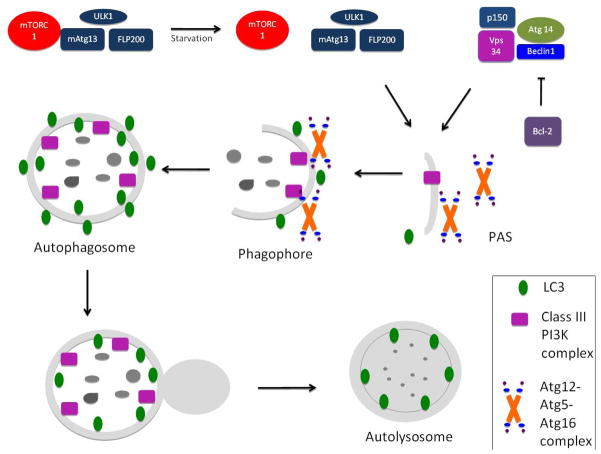
Autophagosome formation requires the ULK1/2-mAtg13-FIP200 complex as well as the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) macromolecular complex, which is composed of the PI3K vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34), beclin1, Atg 14 and p150. This complex recruits two interconnected ubiquitin-like (Ubl) conjugation complexes that are essential for autophagosome formation (Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L1) and elongation (Atg8-LC3) respectively.
Although it is eventually delipidated by Atg4 and recycled, LC3-II is a useful marker of the autophagy membrane because it remains on the inner and outer membrane of the autophagosome until its fusion with the lysosomes. After fusion, the acidic lysosomal hydrolases degrade the engulfed materials. The resultant small molecules are finally transported back to the cytosol for maintenance of cellular homeostasis. The origin of the autophosome membrane remains unknown, although the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondrial membrane have all been implicated.