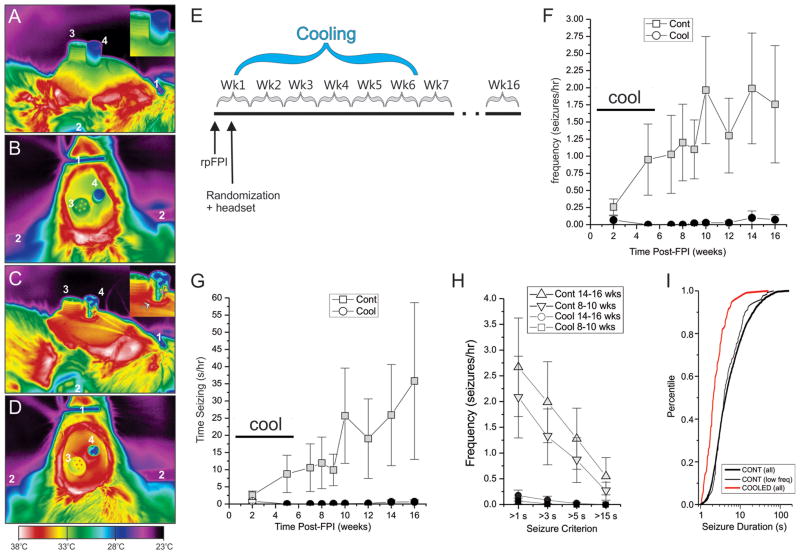
Figure 4. Mild focal cooling prevents the development of CSRSs.
A–D) Thermal images of mock-cooling control headset (A, B) and a D-type cooling headset (C, D). Brain heat is more efficiently dissipated by a D-type headset with a steel rod than a control headset with an acrylic rod. A) Side view. Note the progressive cooling of the acrylic rod and headset with the distance from the brain. B) Top view. Note the cold top surface of the acrylic rod. C) Side view. Note the vertical artifact on the rod due to reflected light (gray arrow), and the ring of hot acrylic surrounding the base of the metal rod (white arrow). D) Top view. Note the ring of hot acrylic surrounding the steel rod, and the overall higher temperature of the whole headset compared to B. Throughout: 1= nose bar; 2= ear cone; 3= ECoG pedestal; 4=acrylic or steel rod. E) Schematic of the experimental protocol. Headsets for cooling and ECoG recordings were implanted 3 days post-injury. Cooling rods were replaced with acrylic rods 5 weeks later. F–G) seizure frequency (F) and time spent seizing (G) are virtually abolished in treated rats compared to controls both during and after treatment termination. Plots show data for seizures longer than 3s. H) Seizure-preventive effect of mild cooling shown for different duration-based seizure definitions in control and treated rats during weeks 8–10 and 14–16 post-injury. The effect is not sensitive to seizure definition. Statistical significance is color coded: black filled symbols indicate a statistically significant difference from the time-matched control (gray symbols). I) Cumulative frequency histograms of seizure durations actually observed in treated rats (COOLED all), all control rats (CONT all), and control rats with seizure frequencies comparable to those of cooled animals (CONT low freq). Cooling significantly left-shifts the distribution of seizure durations toward briefer seizures compared to both all controls and low seizure frequency controls (both p < 0.001, Kolmogorov-Smirnov).