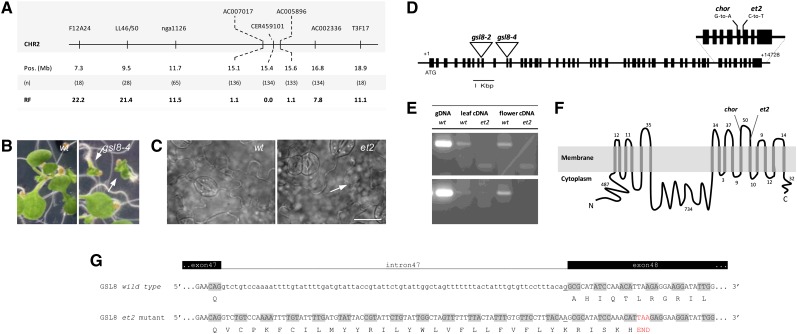
Figure 4.
Positional Cloning of ET2.
(A) Positional mapping of the ET2 locus on the bottom arm of chromosome II. Locations of molecular markers, the number of recombinants (n) and the corresponding recombination frequency (RF) are indicated.
(B) Morphology of 7-d-old seedlings in the wild type (wt) and heterozygous gsl8-4 mutant background (arrows indicate seedling lethal phenotype).
(C) Cell wall pattern and stomatal distribution in wild-type and et2 7-d-old cotyledons. Note the dimeric stomatal cluster and the aberrant cell wall (arrow) in the et2 background. Bar = 20 µm.
(D) GSL8 structure with introns (lines) and exons (boxes) and the position of T-DNA insertions (triangles) and relevant EMS-induced mutations (i.e., et2 and chorus).
(E) RT-PCR analysis using intron-specific primers to monitor the putative retention of intron 47 in et2 cDNA. Three biological replicates were performed and gave a similar result. Sequences of primers used are listed in Supplemental Table 4 online, and the corresponding genomic regions in the GSL8 open reading frame are graphically represented in Supplemental Figure 10 online. gDNA, genomic DNA.
(F) Topology of the GSL8 protein.
(G) Predicted alteration of GSL8 cDNA splicing through the retention of intron 47 in et2 causes the premature establishment of a STOP-codon (red) and results in a truncated GSL8 protein with altered C-terminal amino acid composition.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]