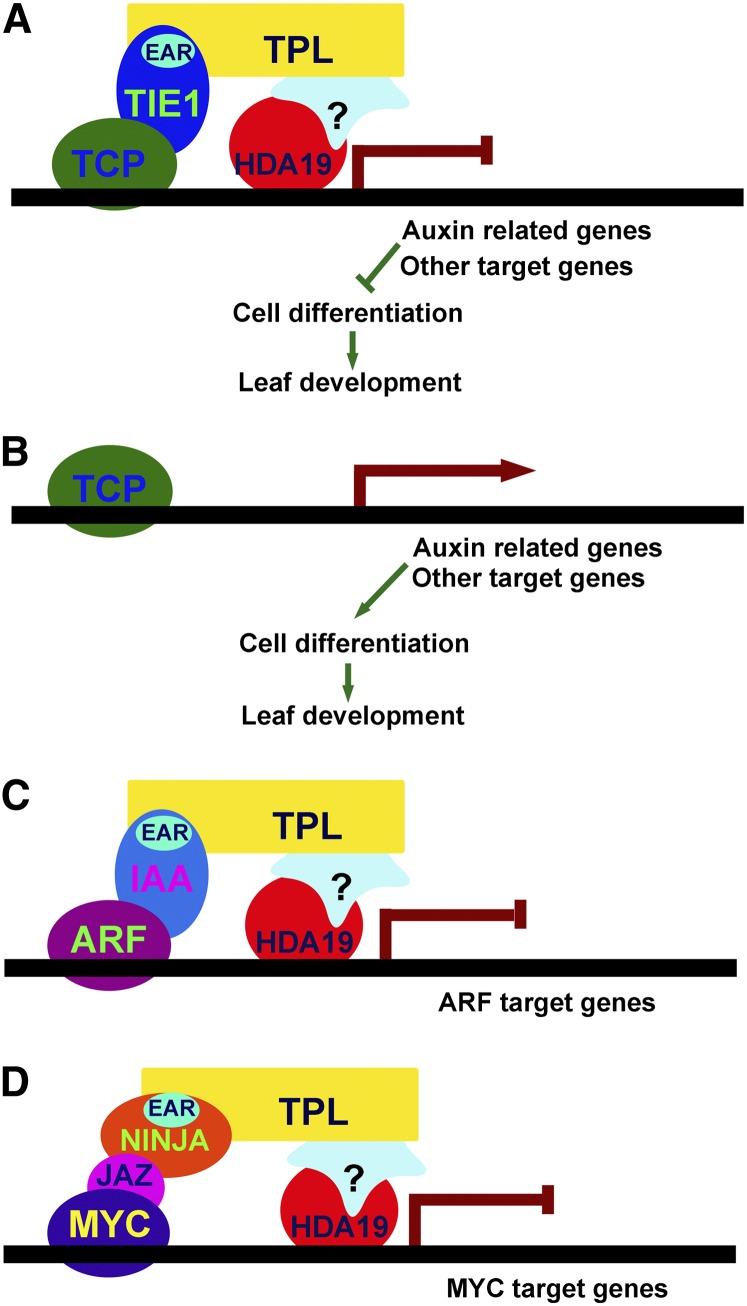
Figure 8.
A Working Model for TIE1 Function.
(A) In the shoot apical meristem and young leaves where TIE1 is expressed, TIE1 interacts with the TCP proteins through the N-terminal portion and also interacts with corepressor TPL/TPRs through the C-terminal EAR motif. The recruitment of TPL/TPRs to TCP proteins inhibits the expression of TCP target genes such as auxin-related genes and other genes that promote cell differentiation. Thus, the cells in young tissues remain undifferentiated.
(B) In old leaves where TIE1 is expressed at low levels or not expressed, TCP activities would not be repressed by TIE1 and the target genes are activated to promote cell differentiation.
(C) The regulation of TCP transcriptional activities by TIE1 during leaf development is similar to the regulation of auxin response factor activities by AUX/IAAs in auxin signaling.
(D) The regulation of TCP transcriptional activities by TIE1 during leaf development resembles the modulation of MYC transcription factor activities by the combination of JAZ and NINJA in JA signaling.