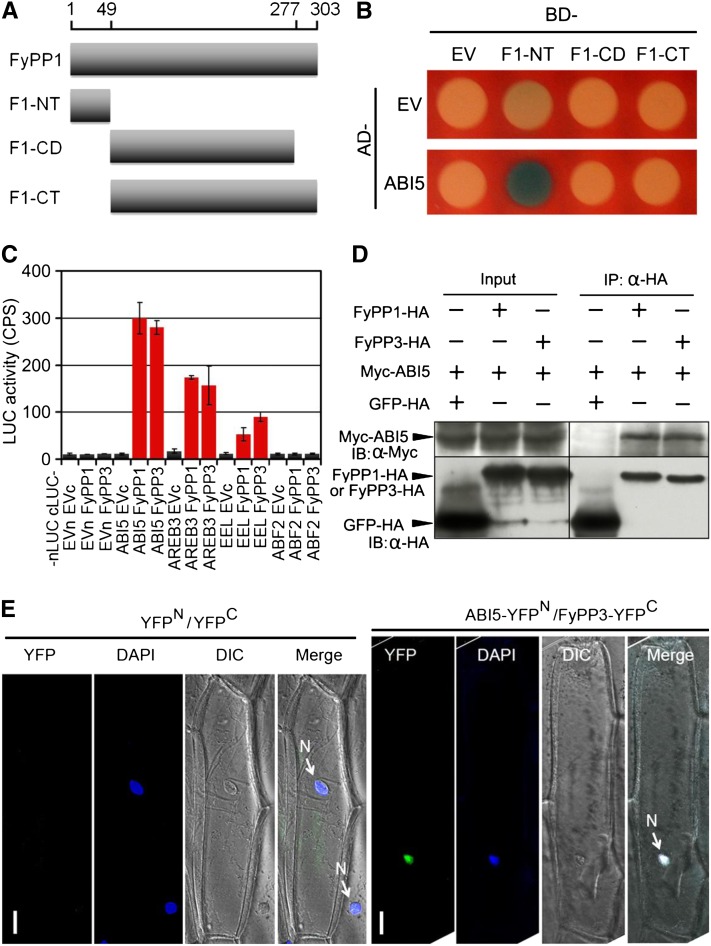
Figure 3.
Protein–Protein Interactions between FyPPs and ABI5.
(A) Diagram of the FyPP1 protein constructs used in Y2H assays. F1-NT, FyPP1 N-terminal region (amino acids 1 to 49); F1-CD, FyPP1 catalytic domain (amino acids 50 to 277); F1-CT, FyPP1 C-terminal region (amino acids 50 to 303).
(B) ABI5 protein interacted with the F1-NT domain of FyPP1 protein in yeast cells. AD, B42 activation domain; BD, LexA DNA binding domain; EV, empty vector control.
(C) LCI assays showing that when fused with nLUC, ABI5 and group I ABI5-like proteins (AREB3 and EEL), but not group II protein (ABF2), interacted with both cLUC-FyPP1 and cLUC-FyPP3 in plant cells. Values are means ± sd, n = 3. EVc, cLUC empty vector; EVn, nLUC empty vector.
(D) Co-IP of ABI5 and FyPP1 or FyPP3 in plant cells. α-HA affinity matrix was used for immunoprecipitation (IP); α-HA and α-Myc antibodies were used for immunoblotting (IB). Input, total protein before immunoprecipitation.
(E) BiFC assays showing that AB15 and FyPP3 interacted in the nucleus. ABI5-YFPN and FyPP3-YFPC fusion proteins were expressed in onion epidermal cells through cobombardment. No YFP signal was observed in onion cells cobombarded with the YFPN (YFP protein N-terminal) and YFPC (YFP protein C-terminal) control plasmids. The nuclei were stained by DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, blue). Bars = 50 μM.