Figure 4.
FyPP Directly Dephosphorylates ABI5.
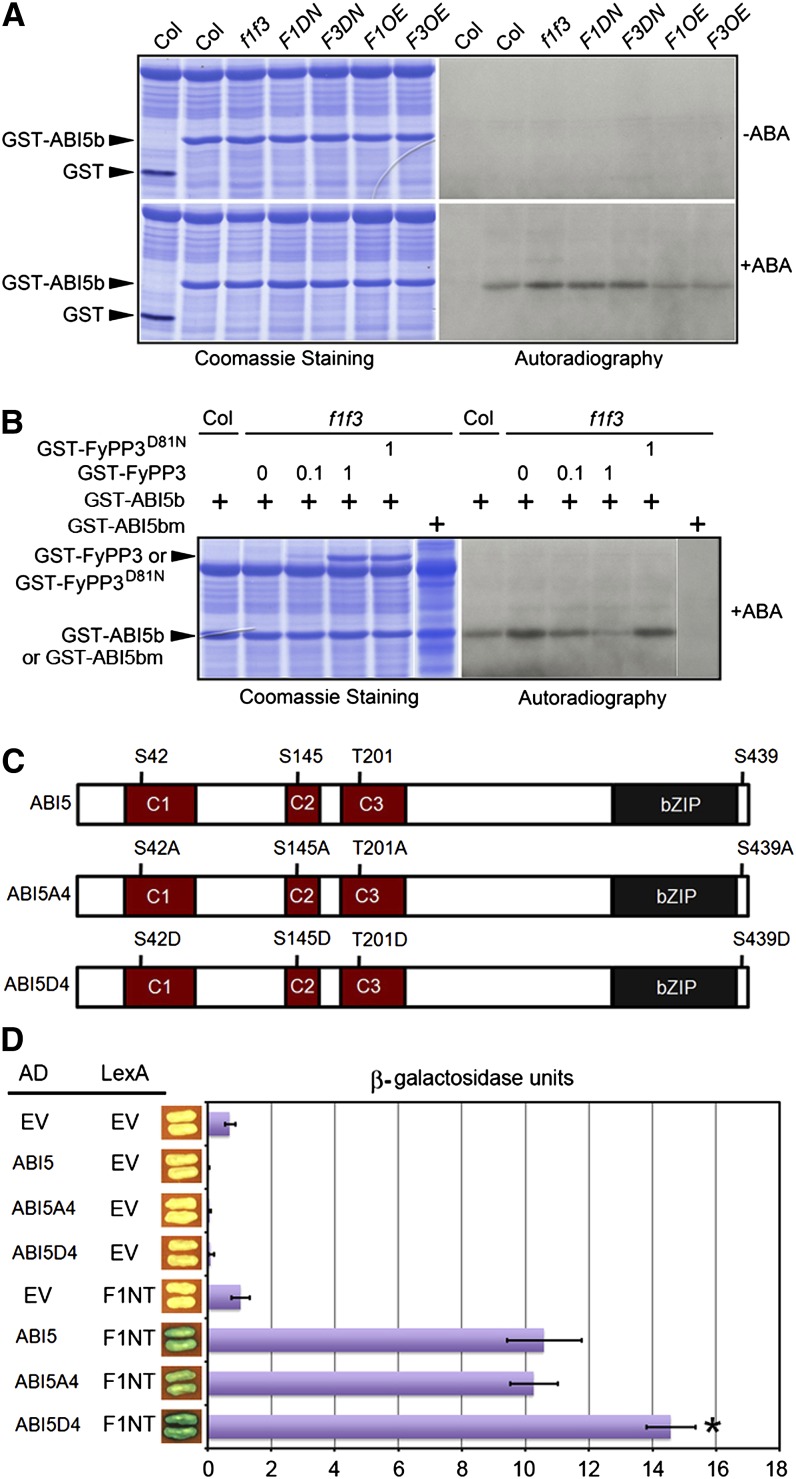
(A) In vitro kinase assay of GST-ABI5b (Ser119-Gln190). In the absence of ABA, there was no detectable phosphorylated GST-ABI5b when treated with the plant extracts derived from Col, f1 f3, F1DN, F3DN, F1OE, and F3OE seedlings. After treatment with ABA, there were increased amounts of phosphorylated GST-ABI5b when incubated with the plant extracts derived from f1 f3, F1DN, and F3DN seedlings, in contrast with the reduced abundance of phosphorylated GST-ABI5b when incubated with the plant extracts derived from F1OE and F3OE seedlings.
(B) In vitro dephosphorylation of GST-ABI5b by GST-FyPP3. GST-FyPP3 reversed the ABA-dependent dephosphorylation of GST-ABI5b treated with the plant extracts derived from f1 f3 seedlings. Increasing amounts of GST-FyPP3 decreased the amount of phosphorylated GST-ABI5b, while the inactive phosphatase (GST-FyPP3D81N) had no effect on the phosphorylation status of GST-ABI5b. A mutant form of ABI5 (GST-ABI5bS145A) was used as a negative control in the experiment. The amounts of GST-FyPP3 and GST-FyPP3D81N proteins used in the assay are indicated by the numbers (0, 0.1, and 1 μg).
(C) Schematic representation of the domain structure of the dephosphorylation mimic mutant ABI5A4 and the phosphorylation mimic mutant ABI5D4 used for the Y2H assays. The labeled Ser (S) and Thr (T) residues were mutated to Ala (A) or Asp (D), respectively.
(D) Y2H assays between FyPP1 N-terminal region (F1NT) and various ABI5 mutants shown in (A). The phosphorylation mimic mutant ABI5D4 showed enhanced interaction with F1NT. Values are means ± sd; n = 3. Asterisks indicate the levels of statistical significance as determined by Student’s t test: *P < 0.02 versus F1NT–ABI5 interaction. EV, empty vector control.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]