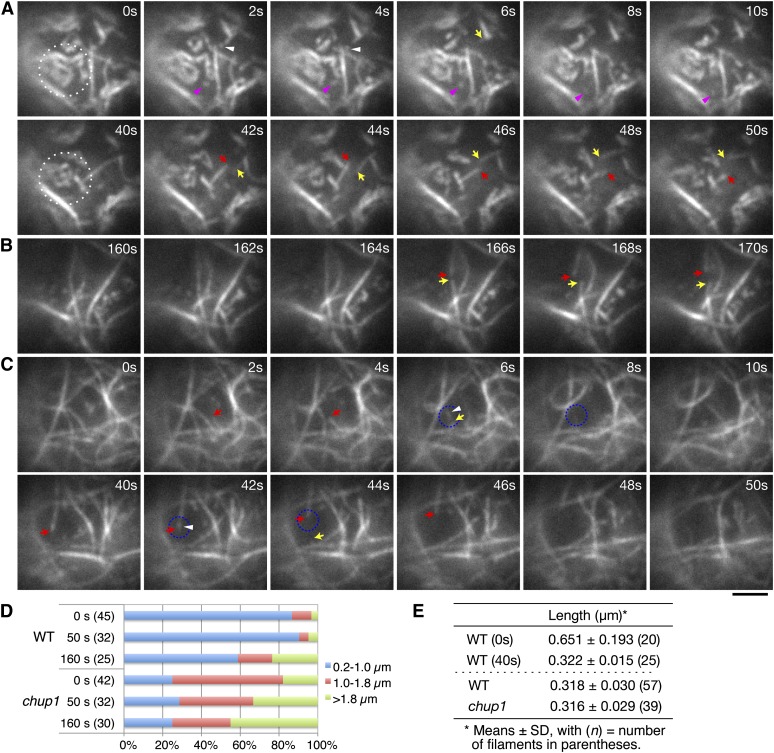
Figure 8.
Comparison of the Reorganization of the Cp-Actin and Cortical Actin Filaments as Observed by TIRFM.
(A) to (C) Actin filament dynamics in wild-type ([A] and [B]) and chup1 mutant (C) protoplasts. Time-lapse images were collected at 0.2-s intervals using TIRFM, and representative images are shown from the time points indicated. Disappearance of the cp-actin filaments was induced by continuous irradiation with 488-nm laser scans for GFP observation, and the cp-actin filaments in the region surrounded by the white dotted circle were carefully followed. Note that actin filaments observed in the chup1 mutant protoplast are not cp-actin filaments, but cortical actin filaments (C). The pink (A) and white ([A] and [C]) arrowheads indicate the small, fragmented cp-actin and cortical actin filaments, respectively. The arrows indicate the ends of the cortical actin filaments that depolymerized at both ends after severing. It is noted that remodeling of the actin filaments in the chup1 mutant protoplasts predominantly occurred via typical stochastic dynamics, including filament buckling and straightening events. See also the full time-lapse series in Supplemental Movie 10 online for the wild type and Supplemental Movie 14 online for the chup1 mutant. Bar = 2 µm.
(D) Quantitative analyses of the cp-actin filaments in the wild-type (WT) and the cortical actin filaments in the chup1 mutant protoplasts. The unit lengths of the actin filaments (see text for details) were measured at 0, 50, and 160 s of irradiation and sorted into three groups (0.2 to 1.0, >1.0 to 1.8, and >1.8 µm). The ratio among the three groups indicates that the short cp-actin filaments are abundant in wild-type cells. The number of cp-actin filaments measured is shown in parentheses.
(E) Average lengths of the cp-actin filaments and fragmented actin filaments. The average lengths of the cp-actin filaments in the wild-type cells were shortened by half between 0 and 40 s (top panel). The shortest lengths of the fragmented actin filaments that did not attach to the other actin filaments were similar for all of the cp-actin filaments (from the wild type) and the cortical actin filaments (from chup1) (bottom panel).