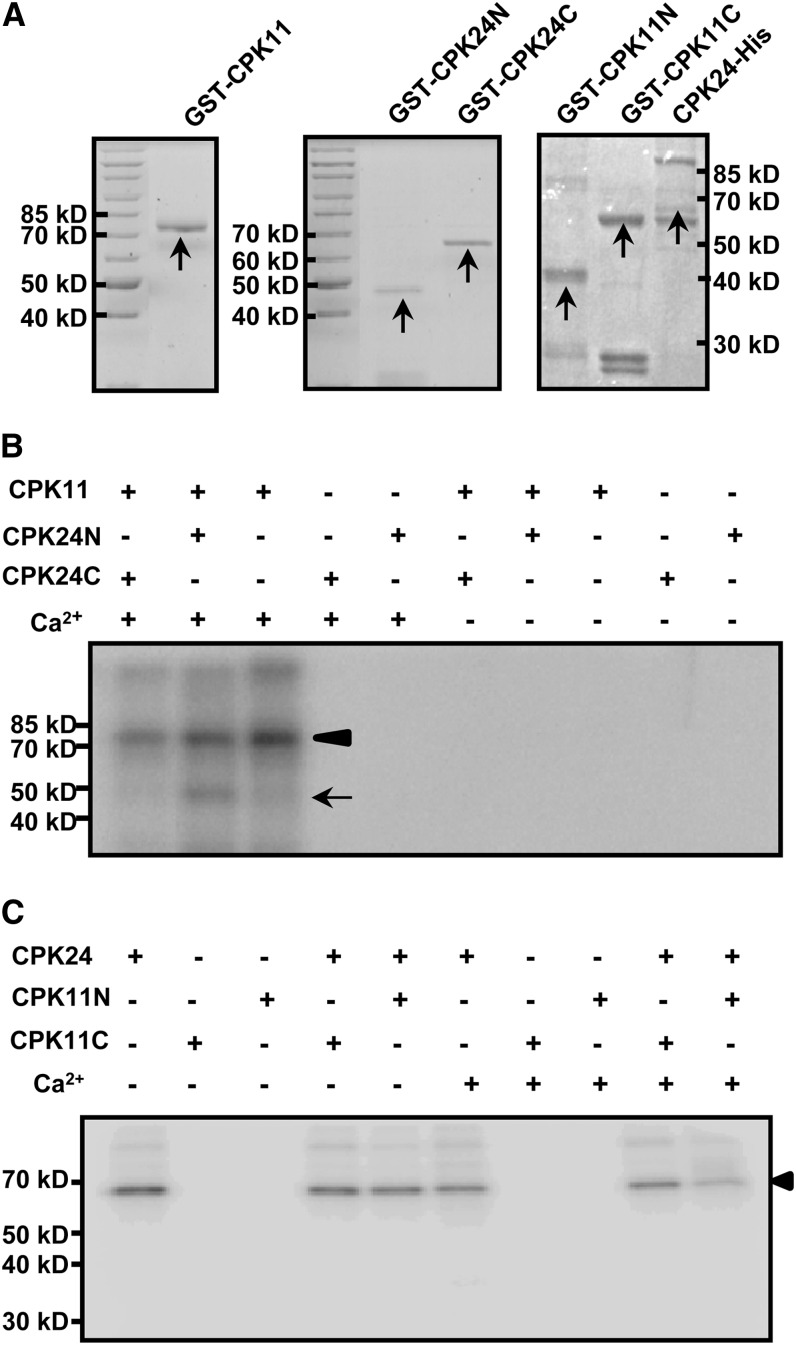
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of CPK24 by CPK11 in Vitro.
(A) Coomassie blue–stained recombinant proteins of CPK11 and CPK24. Purified GST-CPK11 (left panel), GST-CPK24N (N-terminal, from Met-1 to Asn-195 residue; middle panel), GST-CPK24C (C-terminal, from Phe-196 to the end; middle panel), CPK24-His (right panel), GST-CPK11N (N-terminal, from Met-1 to Pro-153 residue; right panel), and GST-CPK11C (C-terminal, from Glu-154 to the end, right panel) are indicated with arrows in Coomassie blue–stained gels.
(B) Phosphorylation of the N terminus of CPK24 by CPK11. Each lane represents an independent reaction and contains 2 μg purified protein (kinase:substrate = 1:1). The arrowhead shows the autophosphorylation of CPK11, and the arrow shows the phosphorylation of CPK24 in the N terminus.
(C) CPK24 cannot phosphorylate CPK11 in vitro. The autoradiogram shows that neither of the truncated CPK11 variants (GST-CPK11N and GST-CPK11C) could be phosphorylated by CPK24 in vitro. The arrowhead shows the autophosphorylation of CPK24.