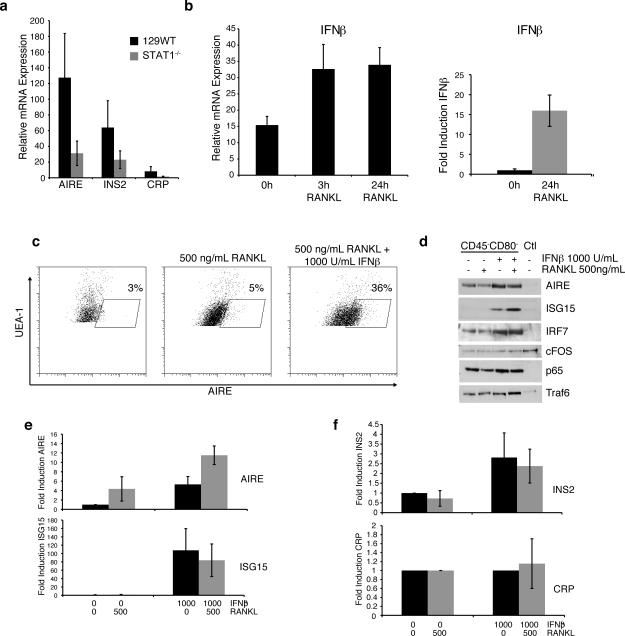
Figure 2. IFNβ promotes AIRE expression following RANKL stimulation.
a) AIRE, INS2, and CRP mRNA levels in thymic stromal cells from WT and STAT1-/- mice (avg+/-sd; n=4) b) Thymic epithelial cells from WT mice (left) or TE-71 cells (right) were stimulated with 500 ng/mL RANKL for the indicated times and IFNβ mRNA levels were determined by qPCR (n = 4). c) Thymic epithelial cells were left untreated or pretreated with 1000 U/mL IFNβ prior to stimulation with 500 ng/mL RANKL for 24 hrs. UEA-1+ cells were analyzed for intracellular AIRE expression by flow cytometry. d) Thymic epithelial cells were depleted of CD80+/hi cells and then stimulated with 500 ng/mL RANKL, 1000 U/mL IFNβ or both for 24hrs. Lysates were probed for AIRE, ISG15, IRF7, cFOS, p65, and Traf6 by Western blotting (representative of three experiments). e) TE-71 cells were treated as indicated, and mRNA levels for AIRE and ISG15 were determined by qPCR (avg+/-sd; n=3). f) Thymic epithelial cells were treated as indicated and mRNA levels for CRP and INS2 were determined by qPCR (avg+/-sd; n=4).