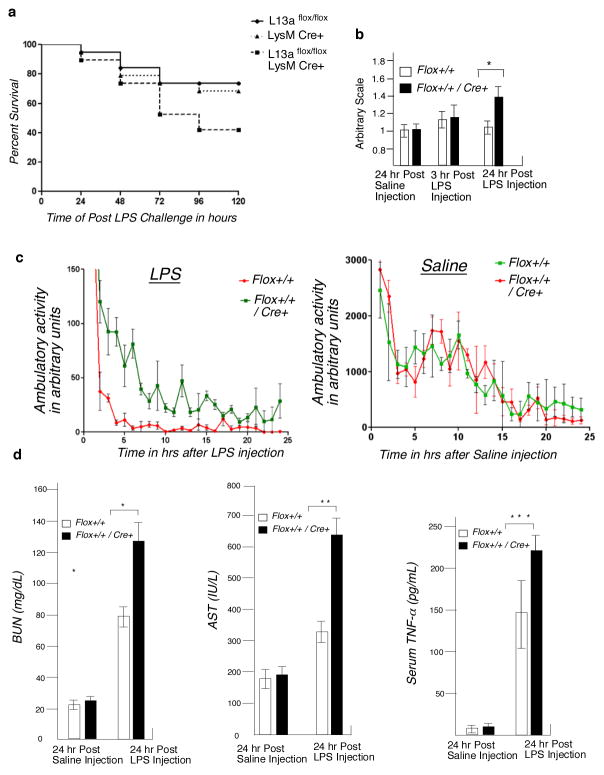
Figure 2. Macrophage-specific L13a KO mice show significantly enhanced susceptibility to endotoxin challenge.
a, Increased death rate of KO mice in response to endotoxin challenge. Age and sex-matched L13aflox/flox, LysMCre+ and L13aflox/floxLysMCre+ mice were challenged with sub-lethal dose of LPS (20 mg/kg) and observed for 120 hours for survival. The survival rate was plotted on Kaplan-Meier survival curves, n=19 in each group, P = 0.042, Log-rank test (Mantel Cox). b, Increase of breath rate of the KO mice upon endotoxin challenge. Control and KO mice were injected with LPS (15 mg/kg) or saline. After 3 and 24 hr post injection breath rate was measured. After 24 hr post saline injection the breath rates for control mice were considered as 1 and the breath rates of all other mice in both time points were plotted on an arbitrary scale. Results are mean ± s.d, n=5, *P = 0.018, two-tailed Student’s t-test. c, Endotoxin challenge causes significant reduction of the ambulatory activity in KO mice. After LPS challenge (15 mg/kg) the ambulatory activities of the KO and control mice were measured for a period of 25 hours using a device equipped to sense the number of sequential laser beam breaks in two dimensions. The ambulatory activities were plotted using arbitrary scale. Results are mean ± s.d, n=8, P = 0.049, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. d, KO mice showed increase serum level of the markers of inflammation. Serum levels of BUN, AST and TNF-α in mice were measured after 8 hours of LPS challenge (15 mg/kg). Results are mean ± s.d, n=4, *P = 0.011, **P = 0.004, ***P = 0.032, two-tailed Student’s t-test.