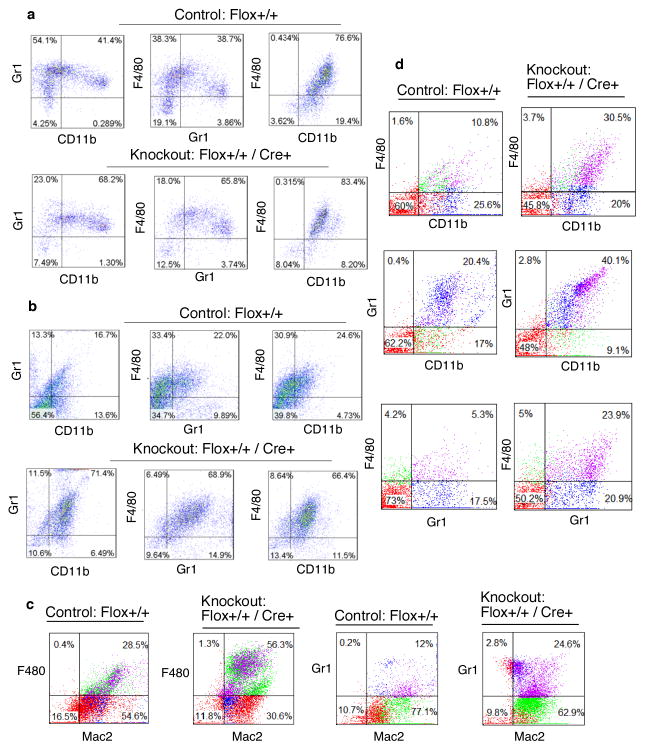
Figure 4. Increased infiltration of immune cells in the peritoneum and higher abundance of splenic leukocytes in the KO mice upon endotoxin challenge.
a, b Enhanced infiltration of leukocytes in the peritoneum of the KO mice in response to thioglycollate and LPS treatment. Increased infiltration of Gr1-CD11b, F4/80-Gr1 and F4/80-CD11b double positive cells in the peritoneal cavity of the KO mice 48 hr after thioglycollate (a) and 24 hr after LPS treatment (15 mg/kg) (b). Results showing the quantitation of the infiltrates of the double positive cells 48 and 24 hr after thioglycollate and LPS treatment respectively from 4 independent experiments with statistical significance shown in supplementary Fig. S1a. c, Increased infiltration of F4/80-Mac2 and Gr1-Mac2 double positive cells in the peritoneum of the KO mice 24 hr after LPS treatment, for quantitation see supplementary Fig. S1b. d, Increased abundance of splenic leukocytes in the KO mice in response to LPS treatment. Control and KO mice were injected with LPS (15 mg/kg), 48 hr after LPS administration leukocytes were harvested from spleen following RBC lysis. F4/80-CD11b, Gr1-CD11b and F4/80-Gr1 double positive cells were quantified by FACS, for quantitation see supplementary Fig. S1c.