Fig. 1.
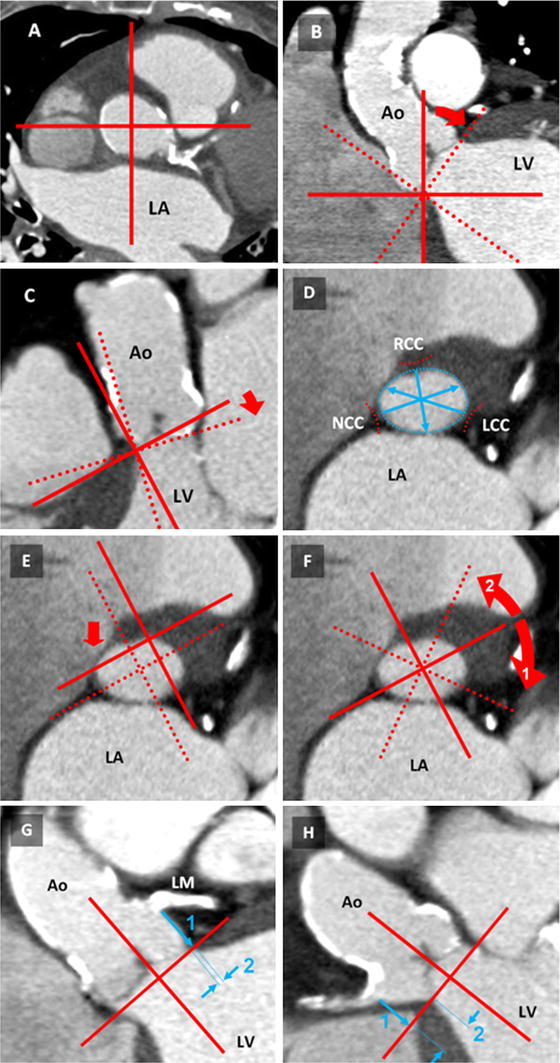
Aortic root measurement procedure. A To begin, the crosshair was placed in the aorta in a transverse section (here at the level of the sino-tubular junction) B In the coronal view, the crosshair was moved to the most basal attachment of any cusp (here: NCC). The crosshair was rotated until one plane reached the corresponding part of the opposite cusp (here: LCC). C In the sagittal view, the same plane was adapted to the next basal cusp attachment (here: RCC). Control of the plane position obtained by scrolling through the image stack. D In the oblique transverse view, the aortic annulus was displayed and used for diameter measurements including the effective diameter. E For coronary ostia measurements, the crosshair was placed in the center of the aortic annulus and rotated until (F) the coronary ostia of the LCA (1) and RCA (2) appeared in the corresponding coronal or sagittal view. G In the plane displaying the LCA ostium, the distance to the aortic annulus was measured (1). Additionally, LCA to LSC (2) was assessed. H The RCA ostium distance (1) and the RCA LSC (2) were measured similarly as in step F. Ao ascending aorta, LV left ventricle, LA left atrium, LM left main, RCA right coronary artery, RCC/LCC/NCC right-/left-/non-coronary valve cusp, LSC lateral shift of the coronary ostia
