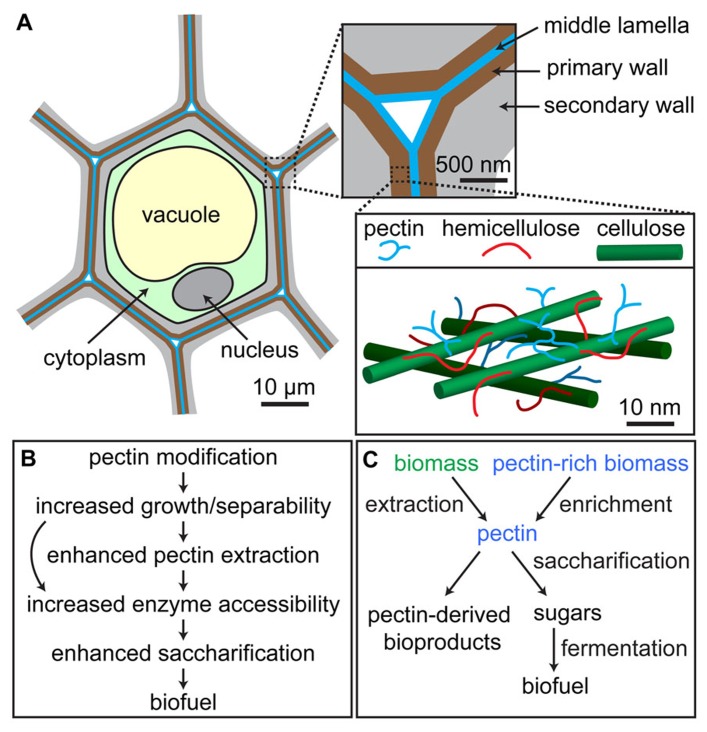
FIGURE 1.
Location and roles of pectins in biomass. (A) Schematic of plant cell showing arrangement of cell walls; pectin is abundant in the primary walls synthesized by growing cells (brown) and the middle lamella that adheres adjacent cells (blue), but is also present in lower amounts in secondary walls produced after the cessation of growth (gray). Inset at lower right is a simplified model of the primary cell wall showing one possible arrangement of cellulose microfibrils (green), hemicellulose (red), and pectin (blue). (B) Pectin-rich biomass can be derived from lignocellulosic feedstocks or naturally pectin-rich plant material, after which it can be processed into pectin-derived high-value bioproducts and/or saccharified and fermented into biofuel. (C) Potential positive impacts of pectin modification in bioenergy crop plants on biomass processing. In some cases, pectin modification might allow for the elimination of processing steps, such as pectin extraction (curved arrow in B).