Table 3.
Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Photoinduced Cleavage of N–N Bondsa

| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | Product | Yield (%) |
| 1 |
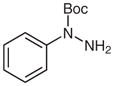 1c |
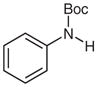 2c |
82 |
| 2 |
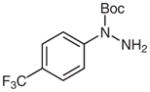 1d |
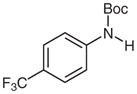 2d |
81 |
| 3 |
 1e |
 2e |
54 |
| 4 |
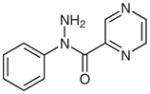 1f |
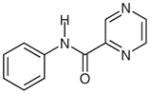 2f |
47 |
| 5 |
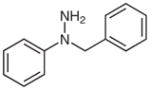 1g |
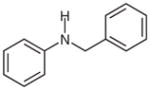 2g |
68b |
| 6 |
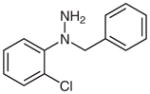 1h |
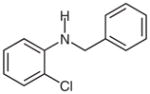 2h |
51b |
| 7 |
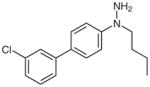 1i |
 2i |
37 |
| 8 |
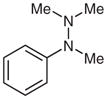 1j |
– | – |
| 9 |
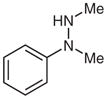 1k |
 2k |
36 |
| 10 |
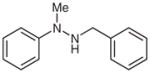 1l |
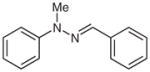 2l |
88 |
| 11 |
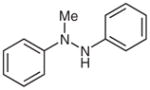 1m |
 2m |
58 |
Reactions were performed on 0.3–0.5 mmol scale in 3–5 mL solvent with 2 mol% 3a. A household 13 W light bulb was used as the light source. Reaction time ranged from 4 to 28 h.
Due to the instability of these hydrazine derivatives, the crude products were subjected to the cleavage reaction directly after Boc-deprotection. The yields given refer to overall yields for the two steps.
