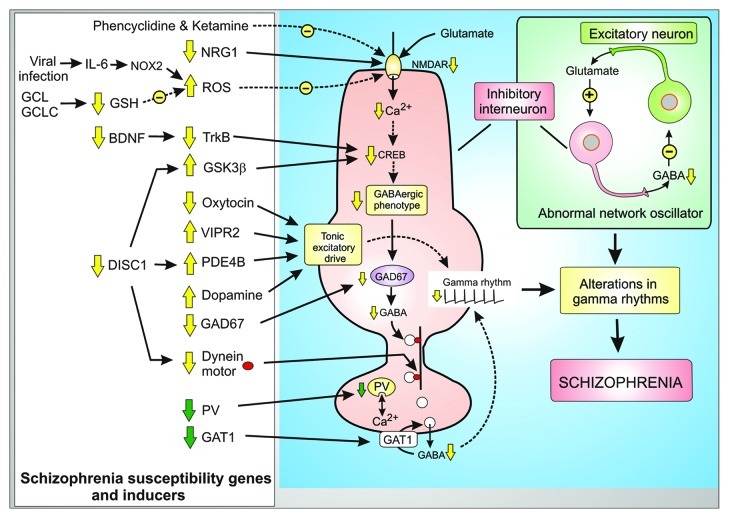
Figure 2. Phenotypic changes and compensatory responses of inhibitory GABAergic interneurons in schizophrenia. Many of the schizophrenia susceptibility genes and pharmacological inducers are associated with the fast spiking GABAergic inhibitory neurons where they act either to decrease the activity of the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) or they play a role in the tonic excitatory drive. All these changes in the activity of these GABAergic neurons interferes with their role in the network oscillator resulting in alterations of the gamma rhythms that are a feature of schizophrenia. Some of the changes are compensatory responses (green arrows) to the genetic modifications.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.