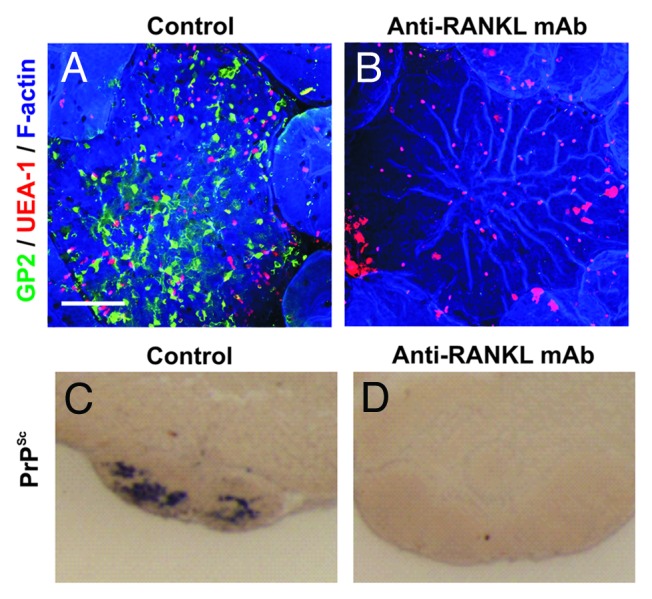
Figure 3. The specific ablation of M cells blocks oral prion pathogenesis. (A&B), Whole-mount immunostaining shows that treatment of mice with anti-RANKL-mAb blocks RANKL-RANKL signaling and specifically depletes M cells (GP2+ UEA-1+ cells) in the FAE of Peyer’s patches. (C&D), In the specific absence of M cells at the time of oral exposure prion accumulation (PrPSc, black) upon FDC in Peyer’s patches is blocked. Adapted from Donaldson et al.66
