Figure 1.
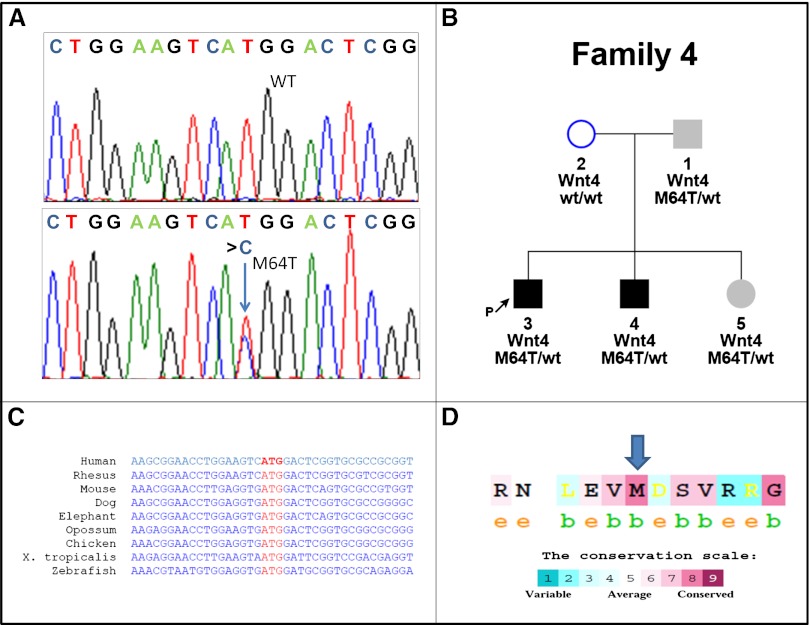
Mutation analysis of the p.M64T, WNT4 variant shows high degree of conservation. (A) Sequence analysis reveals the WNT4 variant caused by heterozygous transition (c.t191c) (lower panel, blue arrow) resulting in amino acid substitution M64T. The wild-type (WT) sequence is given for comparison (upper panel). (B) WNT4 variant is found in patients 1, 3, 4, and 5. Whereas patients 3 and 4 have a clear isolated renal phenotype of severe left renal hypodysplasia, patient 1 has an isolated left renal cyst (sized 12.8×7 mm) in addition to normal BP and normal GFR. Patient 5, age 3 years, has normal pelvic and renal ultrasound results, normal BP, normal GFR, and low morning serum cortisol levels. Incomplete penetrance or variable expression can be considered in this family. Squares indicate male family members and circles female family members; black filled squares indicate that the patients are affected with RHD. Gray filled squares and circles indicate subtle clinical signs. (C) cDNA sequences of human WNT4 are compared with WNT4 orthologs in other species. (D) Conservation scale of WNT4 protein shows the amino acid methionine in position 64 (blue arrow) to be highly conserved (8 of 9), with “b” indicating a buried residue and “e” indicating an exposed residue. Note the high degree of conservation.