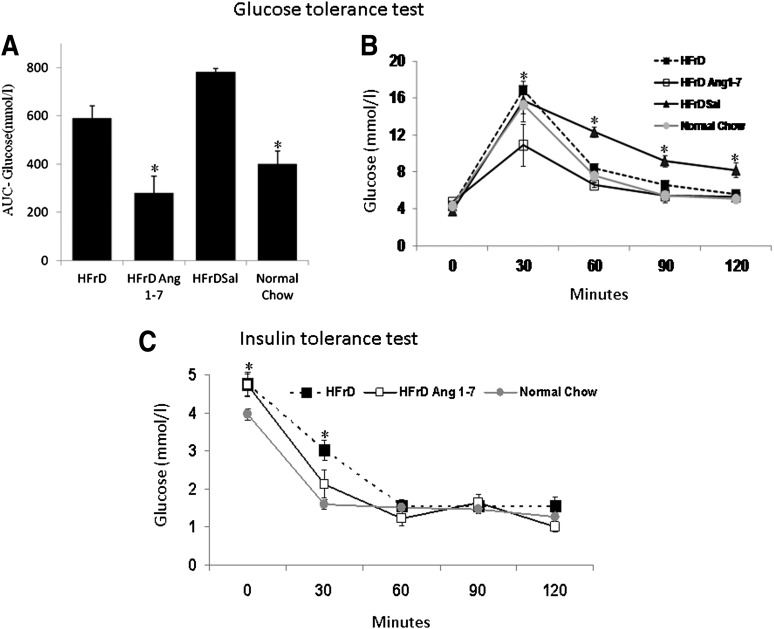
FIG. 1.
Insulin sensitivity tests. A and B: Glucose tolerance test. Ang 1-7–treated rats (n = 6) had normal levels of basal serum glucose and insulin but a significantly attenuated increase in serum glucose response to acute (2 g/kg) intraperitoneal glucose challenge, compared with fructose-fed rats (n = 9, P < 0.05), as revealed by the AUC analysis (A). Glucose levels were measured 30, 60, and 90 min after injection and were significantly reduced by Ang 1-7 at 30, 60, and 90 min postinjection (P < 0.05) (B). Data are presented as the mean value ± SEM. C: Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test. Ang 1-7 rats had increased insulin sensitivity with a more prominent and prolonged hypoglycemic effect of insulin. Changes in basal (t = 0) blood glucose levels after intraperitoneal insulin administration were measured every 30 min over a total period of 120 min. Ang 1-7 treatment led to a significant hypoglycemic reaction at 30 and 120 min post–insulin reduction (P < 0.05). Data are presented as the mean value ± SEM. *P < 0.05.