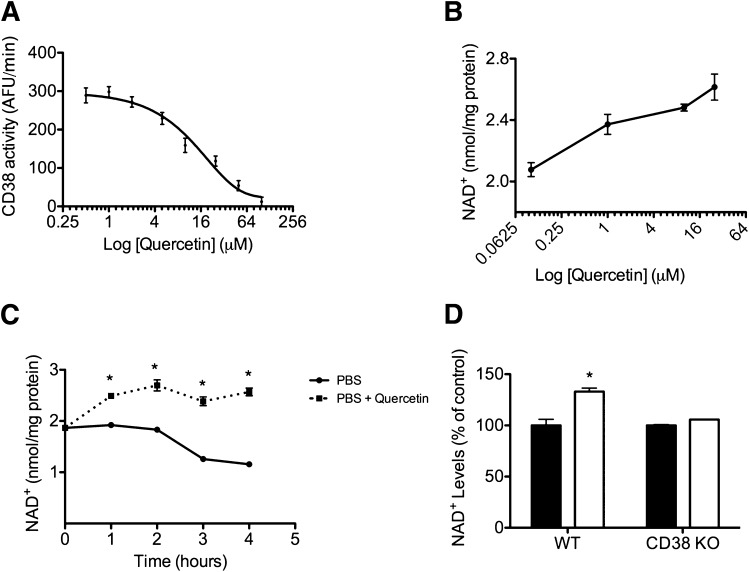
FIG. 4.
CD38 inhibition by quercetin increases NAD+ levels in cells. A: Endogenous CD38 NAD+ase activity was measured in protein lysates from A549 cells. Quercetin was used in the 0.5–100 μmol/L concentration range. Each measurement was done in triplicate. Data points were fitted to a standard competitive inhibition curve using a nonlinear regression program (GraphPad Prism) to yield the IC50 value. B: NAD+ dose-response curve in A549 cells treated with quercetin. Cells were incubated with quercetin for 6 h before NAD+ extraction. *P < 0.05, n = 3. C: NAD+ time course in A549 cells incubated in PBS (●) or in PBS plus quercetin (50 μmol/L) (■). *P < 0.05, n = 3. D: Intracellular NAD+ levels in wild-type (WT) and CD38 knockout (KO) MEFs treated with vehicle (control) (■) or with quercetin (50 μmol/L) (□) for 6 h. NAD+ levels were expressed as percent of change with respect to the control for both cells. Total NAD+ levels were significantly higher in CD38 knockout MEFs. (See Fig. 2F.) *P < 0.05, n = 3.