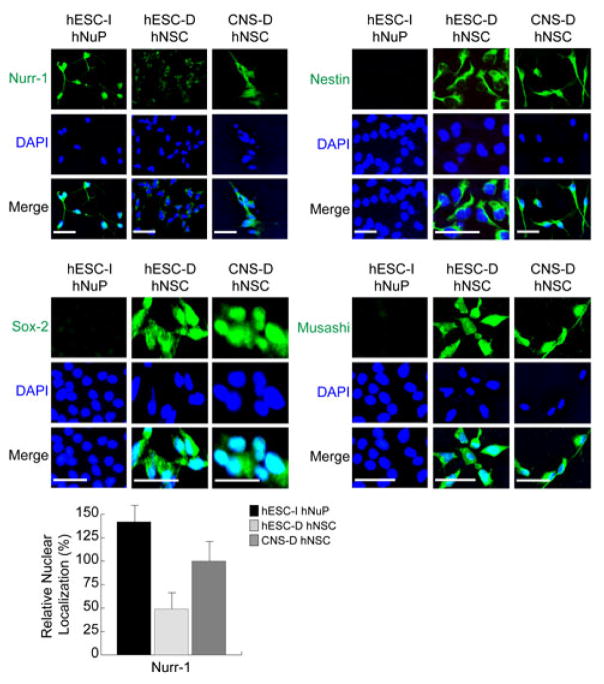
Figure 1. The in vitro neuroectoderm-derived nuclear-Nurr1-positive hESC-I hNuPs do not express the canonical hNSC markers.
hESC-I hNuPs display strong expression and nuclear localization of Nurr-1, compared to fetal CNS-derived hNSCs (CNS-D hNSCs) that show moderate expression and nuclear localization of Nurr-1 and hESC-derived hNSCs (hESC-D hNSCs) that show cell-surface and cytoplasm localization of Nurr-1. hESC-I hNuPs did not express the canonical early neural lineage stem/progenitor cell markers of hNSCs, including Nestin, Musashi, and Sox-2, compared to the two neuroepithelial-like nestin-positive hNSCs either derived from hESCs or CNS. The relative nuclear localization of Nurr1 in these human stem cell derivatives was further verified by quantitative intracellular imaging analysis. DAPI stains nuclei. The nuclear localization of Nurr1 in CNS-D hNSCs is set at 100%. Scale bars: 5 μm.