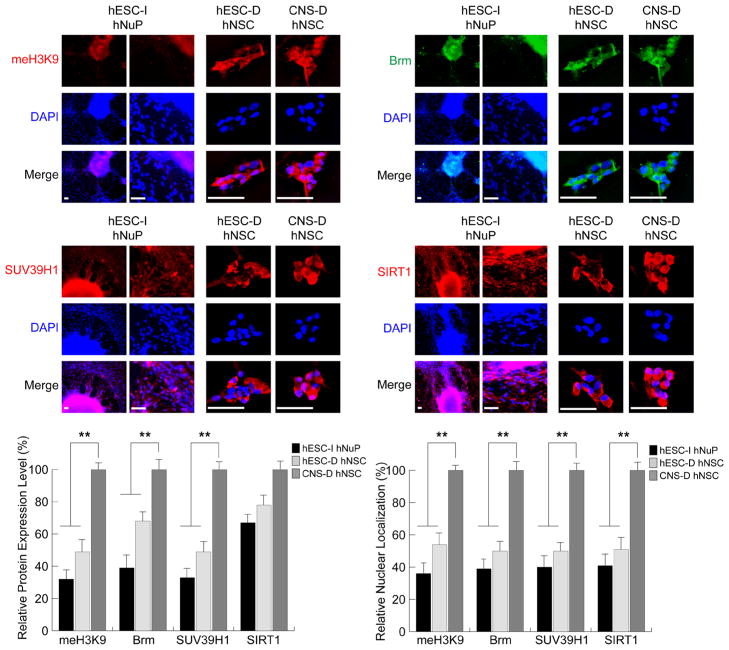
Figure 3. Repressive chromatin remodeling factors regulating histone H3K9 methylation and mediating chromatin-silencing are inactive in hESC-I hNuPs.
The weak expression and cytoplasmic localization of repressive chromatin remodeling factors in hESC-I hNuPs, including H3K9 methylated histones, Brm, SUV39H1, and SIRT1, similar to the expression patterns in hESC-derived hNSCs. In contrast, the CNS-D hNSCs display strong expression and nuclear location of these repressive chromatin modifiers. DAPI stains nuclei. Quantitative intracellular imaging analysis of expression levels and nuclear localization in these human stem cell derivatives confirmed the spatial and temporal patterns of these chromatin-modifying molecules. The expression levels and nuclear localization of these repressive chromatin-modifying molecules in these human stem cell derivatives were quantified and plotted as relative levels in comparison to their expression levels and nuclear localization in CNS-D hNSCs. The expression levels and nuclear localization of these repressive chromosomal proteins in CNS-D hNSCs are set at 100%. Scale bars: 5 μm. Quantification data are presented as Mean ± SD; Statistical significance was defined as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.