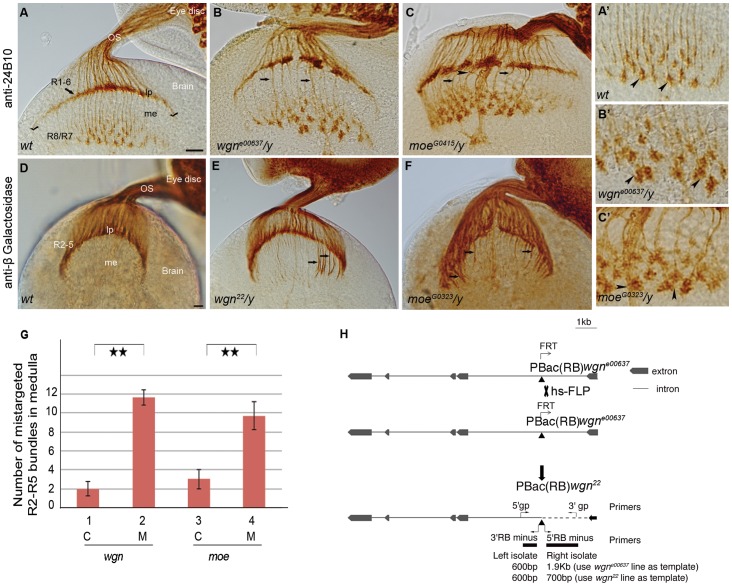
Figure 1. wgn or moe mutation results in R cell axonal targeting defects.
(A–C) Eye-brain complexes of third-instar larvae were stained with 24B10 to visualize all R cell axons. (D–F) Samples were labeled with Ro-tau-LacZ marker and stained by anti-beta galactosidase to visualize R2–R5 axons. (A′–C′) Magnified view of medullar areas in A–C. (A) In wild-type flies, R1-6 growth cones terminated in the lamina to form the lamina plexus (seen as a smooth line, stretching between two check marks in A), while R7 and R8 axons projected into the medulla. R7 and R8 growth cones expanded to form a regular array of non-overlapping growth cones (also see magnified view in A′). In wgne00637/y (B) and moeG0415/y (C) mutants, the lamina plexus was disrupted and the termination fields in the medulla were disorganized and contained many thick wandering bundles (arrows). The growth cones within the medulla were enlarged and overlapped (arrow heads in B′ and C′). (G) Quantifications of mistargeted R2–R5 axon bundles projected into medulla in control, wgn and moe mutant animals. Double stars: P < 0.001; Student T tests, two tails. Error bars denote s.e.m. Genotypes in (G): #1(wgn22/+; rtl/+); #2 (wgn22/y; rtl/+); #3 (moeG0323/+; rtl/+); #4 (moeG0323/y; rtl/+). (H) A diagram illustrating the generating of wgn22 mutant. The P element insertion site in the wgne00637 strain is located in the first intron of wgn at X:18526488 in the minus orientation (indicated by the point upward triangle). FRT-mediated recombination of the wgne00637 strain resulted in production of the wgn22 recombinant line in which the P element remained but deletion of approximately 1200 base pairs was introduced. Abbreviations: lp, lamina plexus; me, medulla; OS, optic stalk; rtl, Rough-tau-LacZ; C, control; M, mutant; gp, genomic primer; hs-FLP, heat shock flippase. Scale bars: A–C, 10 µm; D–F, 10 µm.