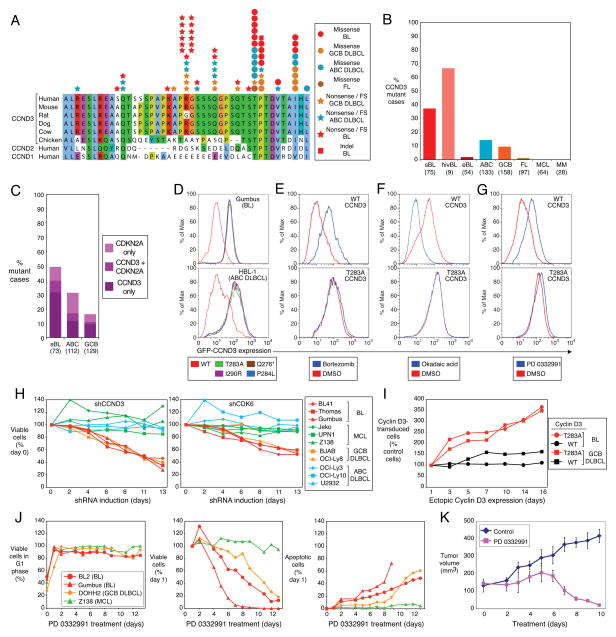
Figure 1. OncogenicCCND3 mutations in Burkitt lymphoma.
a, CCND3 mutations in BL, GCB DLBCL, ABC DLBCL and follicular lymphoma (FL) are shown with respect to amino acid positions 250–292 of protein accession NP_001751. b, Frequencies of CCND3 mutations in different lymphoma subtypes. c, Occurrence of CDKN2A and CCND3 mutations in BL, ABC DLBCL and GCB DLBCL Number of samples analyzed are indicated in parentheses. d, CCND3 mutations increase protein stability. FACS analysis of lymphoma cell lines transduced with mutant or wild type GFP-CCND3 fusion proteins. Cells expressing the different cyclin D3 isoforms had equivalent expression of Lyt2-reporter encoded by the same mRNA as the GFP-CCND3 proteins. e, Mutant cyclin D3 proteins are not degraded by the proteasome. GFP-CCND3-transduced HBL1 cells were cultured overnight in the presence of the proteasomal inhibitor bortezomib (20 nM) and analyzed by FACS. f, Mutant cyclin D3 proteins are not destabilized in response to phosphatase inhibition. BL41 cells expressing GFP-CCND3 proteins were treated for 30 min with the pan-phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid (750 nM) and analyzed by FACS. g, Stability of mutant cyclin D3 proteins is not regulated in the cell cycle. BL41 cells expressing GFP-CCND3 isoforms were treated overnight with the CDK4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991 (1.5 μM), causing arrest at the G1 phase of the cell cycle. FACS analysis indicated that wild type, but not mutant cyclin D3 fusion proteins were stabilized in G1 phase. h, CCND3 and CDK6 shRNAs have selective toxicity for BL and GCB DLBCL cell lines. Shown is the fraction of GFP+, shRNA-expressing cells relative to the GFP−, shRNA-negative fraction at the indicated times, normalized to the day 0 values. i, Mutant CCND3 confers a proliferation advantage in lymphoma cells. Endogenous CCND3 was knocked down by induction of a CCND3 shRNA in Gumbus (BL) and BJAB (GCB DLBCL) cells, while different isoforms of GFP-CCND3 were ectopically expressed. The relative number of GFP-CCND3 expressing cells is plotted versus time after shRNA and GFP-CCND3 induction, normalized to day 0. j, Cell cycle block in G1 phase is lethal to BL and GCB DLBCL cell lines. BL, GCB DLBCL and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cell lines were treated with PD 0332991 (1 μM) over indicated time course. G1 phase arrest of viable cells was confirmed using Propidium Iodide (PI) staining and analyzed by FACS (left panel); viable cells were counted using the trypan blue method (middle panel); apoptotic cells were quantified by cleaved PARP/active caspase 3 FACS-staining (right panel). Survival of cells and the fraction of apoptotic cells after PD 0332991 treatment is shown normalized to day 1. Time courses of G1 phase arrest and apoptotic cells were discontinued after day 9 for Gumbus cell line due to the lack of viable cells. All analyses were performed in triplicate. k, Therapeutic potential of the CDK4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991 revealed using a BL xenograft model. Immunodeficient mice bearing established subcutaneous BL xenografts were treated with PD 0332991 (150 mg/kg/day p.o.) for the indicated times. Tumor volumes were estimated by quantitative imaging of luciferase luminescence. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=3).
FS: frameshift