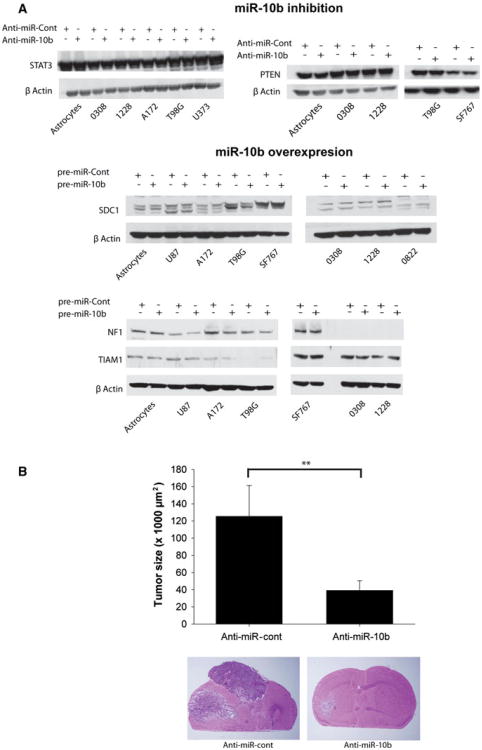
Fig. 5.
miR-10b does not affect the levels of predicted target proteins and miR-10b inhibition significantly inhibits the in vivo growth of human glioblastoma stem cell line-derived xenografts. a Immunoblots showing the absence of changes in miR-10b predicted target proteins' expression upon miR-10b inhibition or miR-10b overexpression in glioblastoma cells and GSCs as well as astrocytes used as a control. The blots were stripped and hybridized for β-Actin as a loading control. b GSCs (1228) were transfected in vitro with 20 nM anti-miR-10b or anti-miR-control for 24 h. 3 × 105 of transfected cells were intracranially implanted into the brains of SCID/BALBc immunodeficient mice (n = 8). Tumor growth was monitored by MRI for 4 weeks. Animals were sacrificed and tumor size was assessed by measuring tumor cross-sectional area on H&E stained slides, with computer-assisted image analysis. The results show that anti-miR-10b treatment significantly inhibits in vivo GSC xenograft growth (** p < 0.01)