Figure 1.
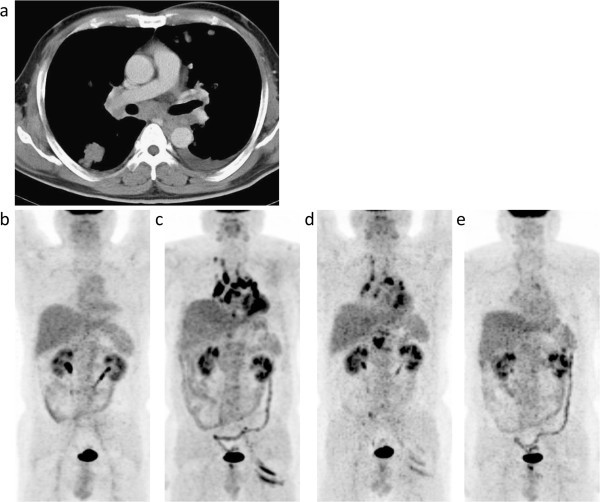
Case 1. A contrast-enhanced CT image taken at the time of the diagnosis of nonseminomatous malignant germ cell tumors with multiple intrathoracic and abdominal lymph nodes and lung metastases (a) and maximum intensity projection (MIP) images of FDG-PET/CT scans that were conducted 3 (b) and 6 years (c) after the completion of antineoplastic therapy and 8 (d) and 15 months (e) after the detection of FDG-avid lesions. (a) CT images before antineoplastic therapy showing metastases in the bilateral hilar and mediastinal nodes and lungs with pleural effusion. (b) No abnormal FDG uptake is observed. (c) Increased FDG uptake is evident in the bilateral hilar and mediastinal nodes (maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) 17.7), abdominal nodes, and the left gluteal muscles. (d, e) A gradual decrease to normal is observed concerning FDG uptake in these lesions.
