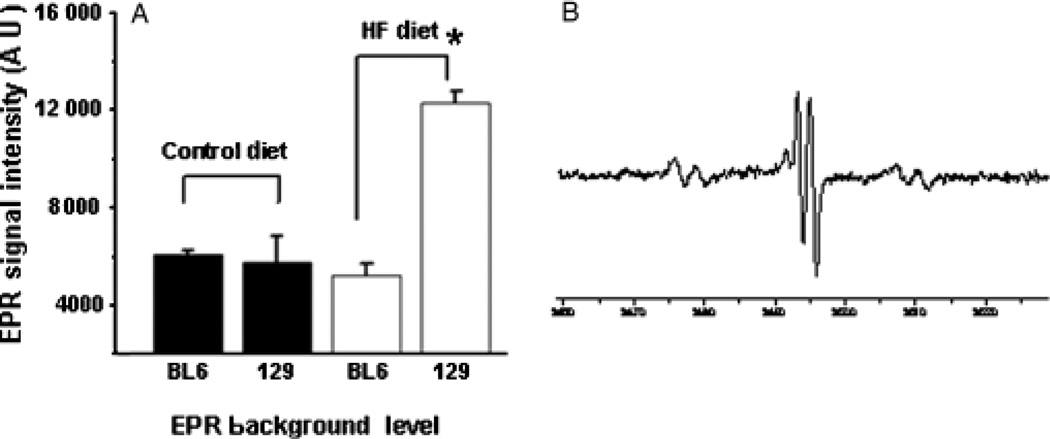
Fig. 2.
Electron spin resonance (ESR) analysis demonstrates strain-related differences in hepatic free radical adduct (reactive oxygen species) (25) production during high-fat (HF) diet treatment. Bile was obtained from randomly selected BL6 and 129/SVJ mice after 6 months of feeding control chow or HF diets (n = 4 mice/group) and analysed for free radical adduct (25) content by ESR. Mean (SEM) results are graphed (A). Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectrum demonstrates typical reactive oxygen species peaks in a representative 129/SVJ mouse (B). *P<0.05 vs BL6 HF-fed group.