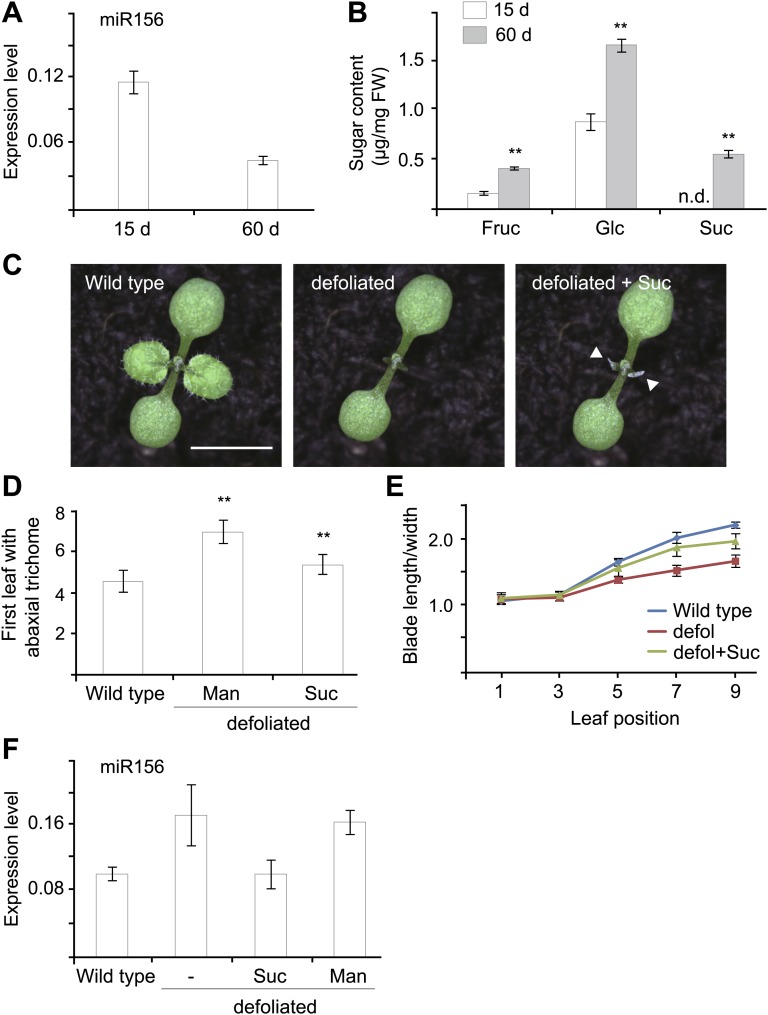
Figure 4. Sugar as a mobile signal to trigger vegetative phase transition.
(A) Expression of miR156 in 15-day-old and 60-day-old wild type plants grown under short day conditions. (B) Sugar measurement. Fifteen-day-old and 60-day-old short day plants were collected at Zeitgeber time 16. The fructose (Fru), glucose (Glc), and sucrose (Suc) content was analyzed by GC-MS and quantified. **Significant difference from 15-day-old wild type plants, Student t-test, p<0.001. Error bars indicate SD. n.d.: undetected; FW: fresh weight. (C) Seven-day-old wild type Arabidopsis seedlings before and after defoliation. Arrows indicate where the lanolin-sucrose (Suc) paste was applied. Scale bar indicates 0.5 cm. (D and E) Seven-day-old wild type seedlings before and after defoliation. Appearance of the first abaxial trichome (D) and the length-to-width ratios of blades (E) were measured. n=10. **Significant difference from wild type, Student t-test, p<0.001. Error bars indicate SE. defol: defoliated; Suc: sucrose. (F) Expression of miR156. Seven-day-old wild type seedlings were defoliated and sucrose (Suc) or mannitol (Man) was applied to the defoliated petioles. The shoot apices were collected for expression analyses 2 days after defoliation.