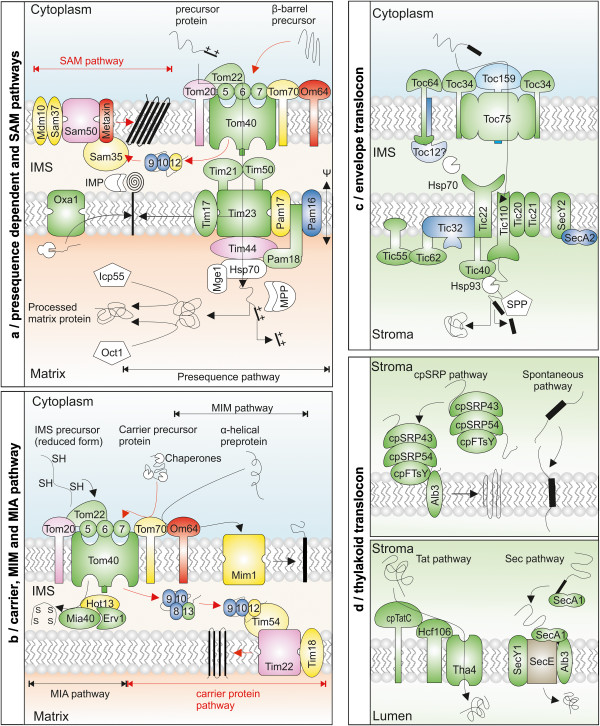
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial and chloroplast protein import machineries. (a,b) Import of mitochondrial proteins generally unifies at TOM complex. Tom20 acts as initial receptor for preproteins and transfers them to Tom22 and Tom40 channel. (a) Presequence pathway: in IMS preproteins interact with Tim50 / Tim21 and Tim17 / Tim23 translocates preproteins across IM assisted by mtHsp70, Tim44, Pam18, 16 and 17. SAM pathway: in IMS Tim9-Tim10 and Tim8-Tim13 guide β-barrel proteins to SAM complex (Sam50, Sam35, Sam37). In plants, Sam35 and Sam37 are likely replaced by metaxin. (b) Carrier pathway: IMPs with cleavable sequence are recognized by OM receptor Tom70 (replaced by OM64 in plants). In IMS Tim9-Tim10 / Tim8-Tim13 guide protein to TIM22 complex, laterally releasing the protein into the membrane. Mia pathway: Mia40 recognizes cysteine residue in IMS preproteins and leads to the formation of a disulfide bond in an Erv1/Hot13-dependent manner. The Mim pathway promotes the insertion of α-helical proteins into the outer membrane. (c) Preproteins bind to Toc64, Toc159 and Toc34, which transfer them to Toc75. Toc64 forms ‘IMS complex’ with Toc12, imsHsp70 and Tic22. Tic110, Tic20 and Tic21 have a discussed translocation-channel function, while Tic62, Tic55 and Tic32 regulate the translocon activity. Tic40, stHsp70 and stHsp93 provide energy for final translocation. (d) cpSRP pathway: cpSRP is composed of cpSRP54 and cpSRP43, which form a transit complex with substrates and targets them to thylakoid membrane via cpFtsY and Alb3. Spontaneous pathway does not require proteinaceous factors. Twin-arginine translocon: TAT signal containing preproteins bind to Hcf6 and cpTatC, leading to the assembly with oligomeric subunit, Tha4 and transient translocon formation. Sec pathway: cpSecA binds to signal sequence and guides it to cpSecY, cpSecE and Alb3. For color code see legend of Figure 2. The question mark on Toc12 indicates that localization of this factor is under debate.