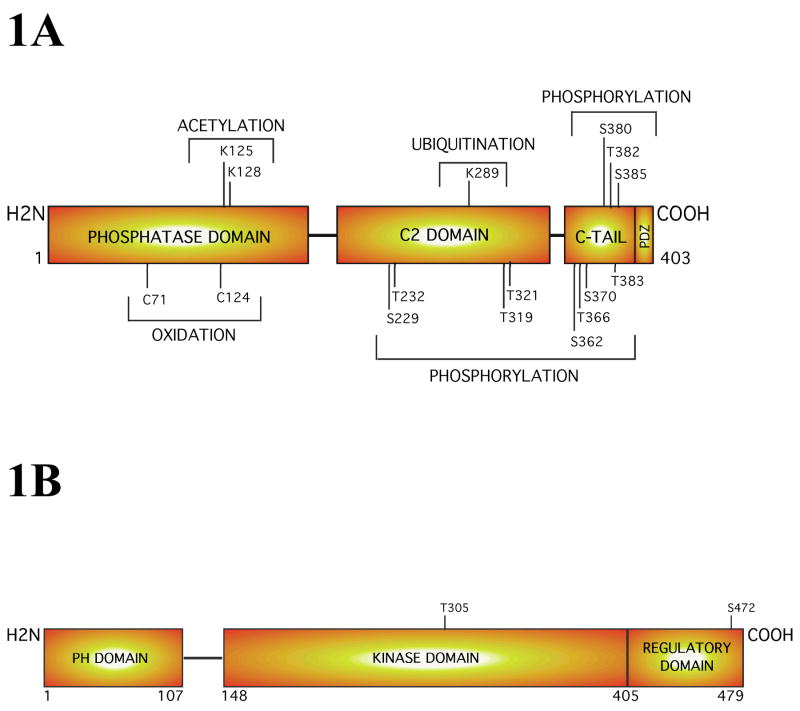
Figure 1. Structure of the PTEN and Akt3 proteins.
1A PTEN, a tumor suppressor protein and lipid phosphatase, is a 55 kDa enzyme containing an N-terminal phosphatase domain, a central C2 domain, and a C-terminal tail. Each domain has sites for post-translational modifications that could involve: acetylation, oxidation, ubiquitination, or phosphorylation, which have potential to regulate PTEN activity. 1B. Structural analysis of Akt3 reveals that this oncogenic survival kinase increasingly active during melanoma progression consists of an N-terminal PH domain, a central kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory motif. Complete activation of this kinase occurs only when the threonine 308 (T308) and serine 472 (S472) gets phosphorylated by PDK1 and a PDK2.