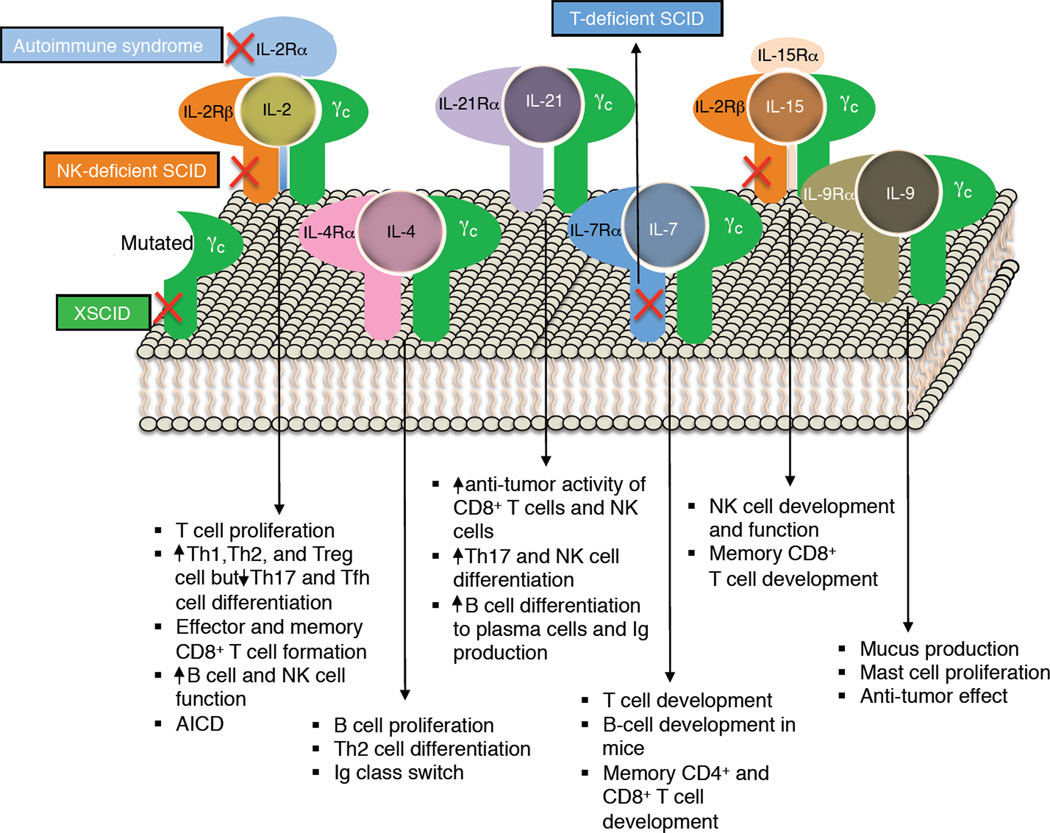
Figure 1. The γc family of cytokines.
Shown are the receptors for IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21, as well as major actions for these cytokines. Crosses in red indicate that mutation of IL2RG gene, which encodes γc, results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans (XSCID, where both T cells and NK cells are greatly diminished [T−B+NK− SCID]), mutation of IL2RA results in an autoimmune syndrome, defective expression of IL2RB results in NK-deficient SCID (where T and B cells remain [T+B+NK− SCID]), and mutation of IL7R causes T-cell selective form of SCID, where B and NK cell numbers are normal (T−B+NK+ SCID). JAK3 is not shown as it interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of γc; however, mutations in JAK3, as noted in the text, cause a T−B+NK− for SCID, like XSCID.