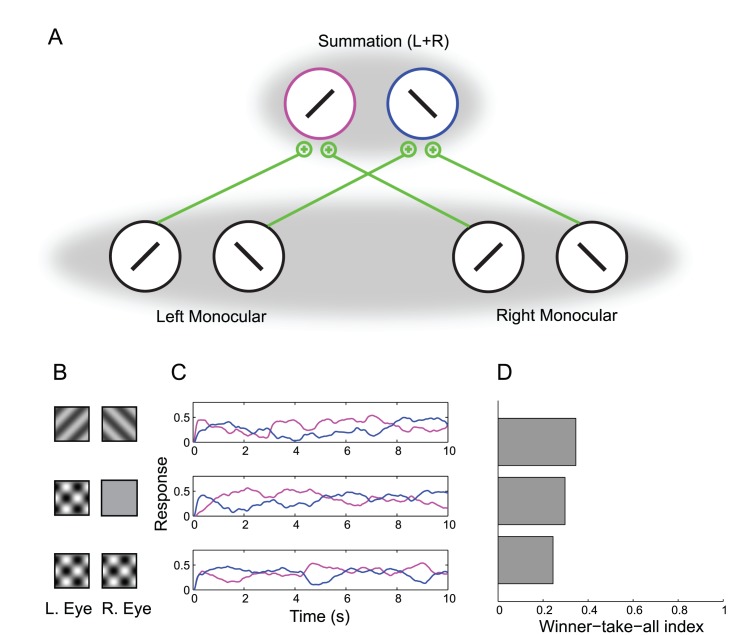
Figure 2. Conventional model.
(A) Schematic. Monocular neurons drive iso-oriented binocular summation neurons with excitatory feedforward connections (green). Mutual inhibition within each layer is implemented by a normalization pool (gray shadows). (B–D) Model simulations. Top row: dichoptic gratings. Middle Row: monocular plaid. Bottom row: binocular plaids. (B) Stimulus conditions. (C) Example response time-courses of the two binocular summation neurons. (D) Winner-take-all (WTA) index. The conventional model shows dichoptic grating rivalry that is only slightly stronger than plaid component rivalry.