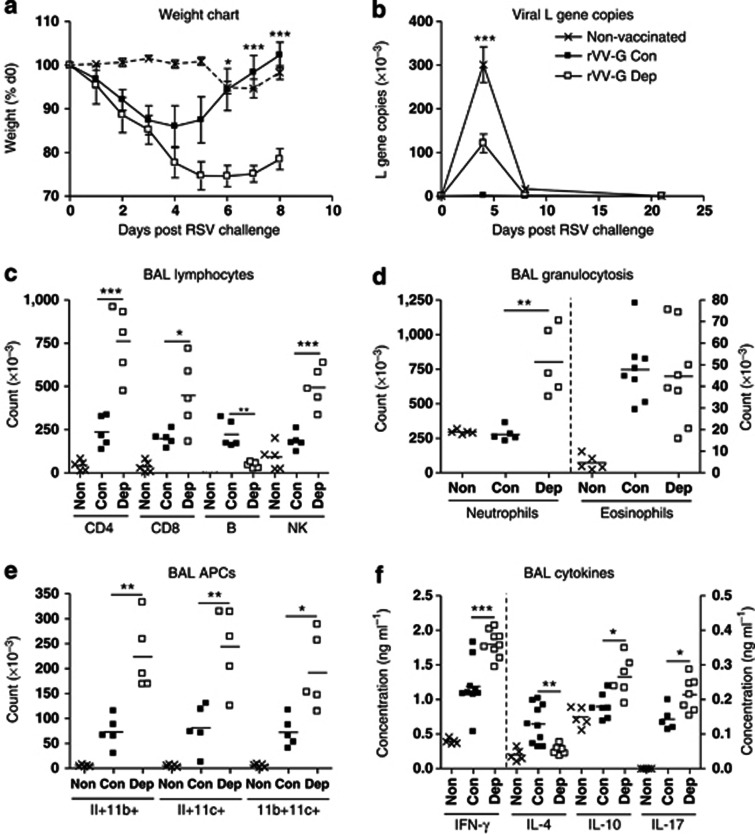
Figure 2.
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) depletion exacerbates immunopathology but compromises viral clearance upon respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) challenge. Mice were immunized with vaccinia virus expressing βgal (Non-vaccinated) or RSV G protein (rVV-G) and treated with αIL-21 antibody (0.5 mg; intraperitoneally; Dep) or isotype control (Con) 1 day before and 2 days after immunization. They were challenged with RSV 14 days later. (a) Mice were weighed daily, and percentage of weight loss was calculated. Lungs were harvested, processed, and RNA extracted as described in Materials and Methods. cDNA was produced by real-time reverse transcriptase–PCR and copies of the RSV L gene were determined by quantitative PCR (Taqman). Plasmids encoding the L gene were used as standards to quantitate L gene copies. (b) Results are expressed as the number of L gene copies. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and lungs were harvested at d5 post challenge. (c) CD4 T cell, CD8 T cell, B cell and NK cell recruitment, (d) granulocyte recruitment, and (e) antigen presenting cell recruitment into BAL fluid was determined by flow cytometry. Cytokines were quantitated in BAL fluid by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (f). Error bars represent s.e.m. The graphs are representative of three independent experiments of five mice per group. Analysis of variance (Tukey's post-test) or Student's t-test result; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. APC, antigen-presenting cell; IFN, interferon; NK, natural killer.