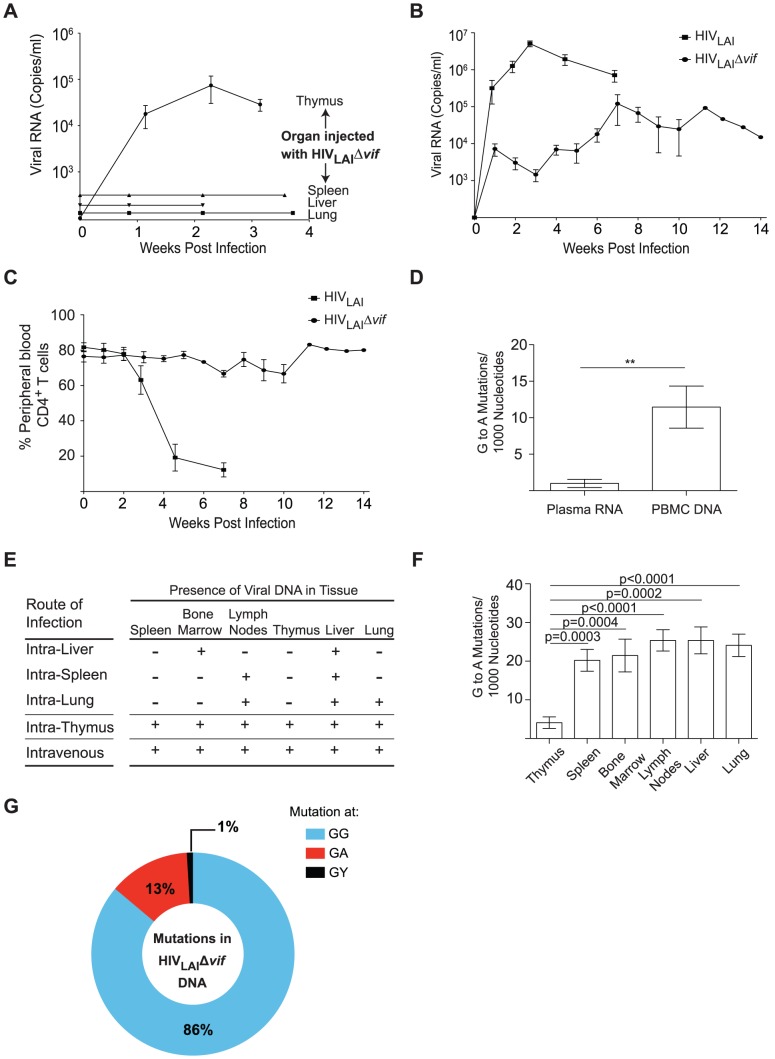
Figure 6. Sustained Vif-independent replication of CXCR4 tropic HIV-1.
(A) Plasma viral load was monitored in NSG-BLT humanized mice infected with 3.6×105 TCIU HIVLAIΔvif directly into the human thymic implant, spleen, liver, or lung. Direct injection of HIVLAIΔvif into the thymus resulted in plasma viremia in 4/4 infections. (B) Longitudinal analysis of plasma viral load in humanized mice infected intravenously with 3.6×105 TCIU of HIVLAIΔvif (n = 7) or 3–9×104 TCIU of wild-type HIVLAI (n = 6). Data represent mean +/− SEM. (C) Longitudinal analysis of the percentage of CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of humanized mice infected in panel B. (D) Comparison of the G to A mutation frequency in the viral RNA from the plasma and the viral DNA from peripheral blood cells from mice intravenously infected with HIVLAIΔvif. Data represent mean +/− SEM from 18 sequences, ** p = 0.0066. (E) Detection of HIV DNA (+) by nested PCR from the tissues of BLT humanized mice in panels A and B. Negative tissues (−) yielded no amplified viral DNA using two independent nested PCR primer sets targeting separate regions of the viral genome. Direct injection of HIVLAIΔvif into the liver, lung or spleen resulted in limited tissue distribution of viral DNA. (F) Comparison of the G to A mutation frequency in viral DNA from the thymus compared to viral DNA from other tissues of mice infected intrathymically (n = 4) and intravenously (n = 7) with HIVLAIΔvif. Data represent mean +/− SEM from 83 sequences. (G) G to A mutational profile of all viral DNA from mice infected with HIVLAIΔvif. Percentages indicate the proportion of G to A mutations occurring at GG (blue), GA (red), or GY (black) sites.