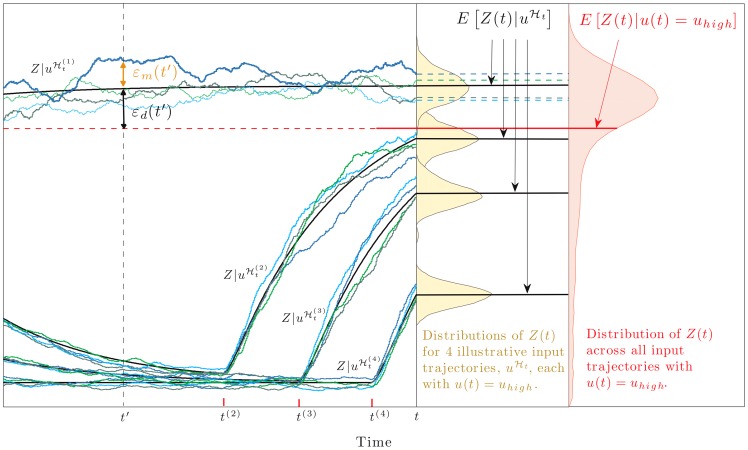
Figure 2. Dynamical error as the difference between two conditional expectations.
To illustrate, we consider a 2-stage model of gene expression with the input,  , equal to the current rate of transcription, and the signal of interest
, equal to the current rate of transcription, and the signal of interest 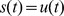 . We model
. We model 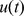 as a 2-state Markov chain and show simulated trajectories of the protein output,
as a 2-state Markov chain and show simulated trajectories of the protein output,  , corresponding to four different input trajectories,
, corresponding to four different input trajectories,  . These input trajectories (or histories) all end at time
. These input trajectories (or histories) all end at time  in the state
in the state  (not shown) and differ according to their times of entry into that state (labelled
(not shown) and differ according to their times of entry into that state (labelled 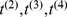 on the time axis;
on the time axis;  is off figure).
is off figure). 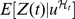 (black lines) is the average value of
(black lines) is the average value of  at time
at time  given a particular history of the input
given a particular history of the input  : the random deviation of
: the random deviation of  around this average is the mechanistic error
around this average is the mechanistic error 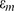 (shown at time
(shown at time  for the first realisation of
for the first realisation of 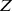 ).
).  is the average or mean value of
is the average or mean value of 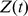 given that the trajectory of
given that the trajectory of  ends in the state
ends in the state 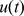 at time
at time  .
.  (red line) can be obtained by averaging the values of
(red line) can be obtained by averaging the values of  over all histories of
over all histories of  ending in
ending in 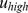 . The mean is less than the mode of the distribution for
. The mean is less than the mode of the distribution for 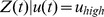 because of the distribution's long tail.
because of the distribution's long tail.  , not shown, is obtained analogously. The dynamical error,
, not shown, is obtained analogously. The dynamical error,  , is the difference between
, is the difference between  and
and 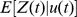 and is shown here for the first trajectory,
and is shown here for the first trajectory,  . Fig. 3B shows data from an identical simulation model (all rate parameters here as detailed in Fig. 3B).
. Fig. 3B shows data from an identical simulation model (all rate parameters here as detailed in Fig. 3B).