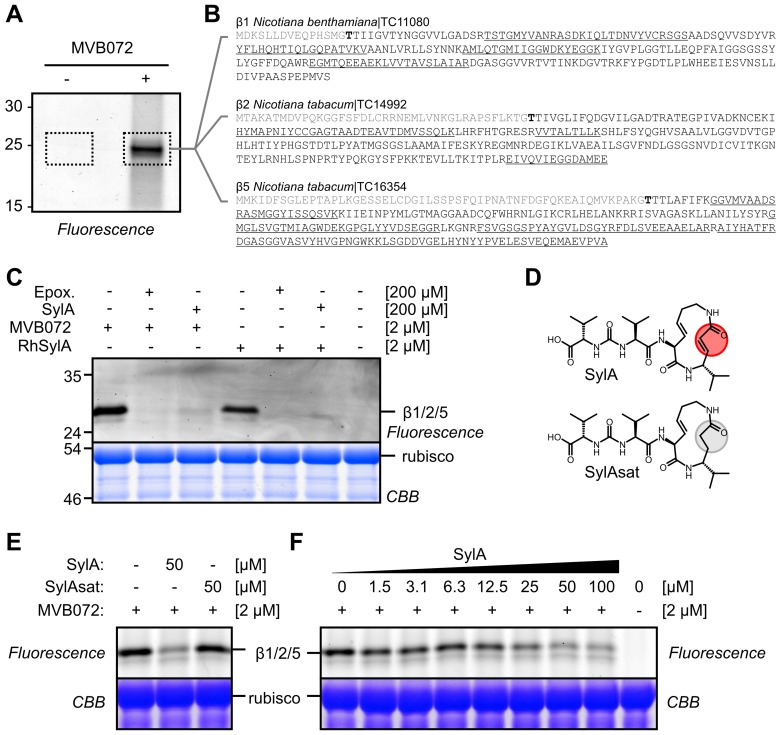
Figure 3. SylA targets the proteasome of N. benthamiana.
(A) MVB072 labels the catalytic proteasome subunits in N. benthamiana leaf extracts. Leaf extract of N. benthamiana was incubated with or without MVB072, an epoxomicin-based probe carrying both biotin and BODIPY. Biotinylated proteins were purified and detected by in-gel fluorescence scanning. (B) Proteins identified by mass spectrometry. In-gel trypsin digests (dashed areas) were analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry. Identified peptides are underlined in the sequences of the β1, β2, and β5 catalytic subunits of the proteasome. None of these peptides were found in the no-probe-control. No peptides were from the propeptide (grey) or the mature N-terminus, containing the catalytic Thr (bold). (C) SylA targets the proteasome of N. benthamiana. Leaf extracts of N. benthamiana were preincubated with 200 µM epoxomicin (Epox.) or SylA for 30 min and then labeled for 2 h with 2 µM MVB072 or RhSylA. Labeled proteins were detected by in-gel fluorescence scanning, and proteins were stained with Coomassie blue. (D) Structures of SylA and SylAsat. SylA has a Michael system in the ring that reacts with the catalytic Thr residues of the proteasome. This Michael system is absent in SylAsat due to saturation of the double bond. (E) SylAsat does not fully inhibit the proteasome. Leaf extracts were preincubated with 50 µM SylA and SylAsat and labeled with MVB072. Proteins were separated on protein gels and detected by fluorescence scanning and Coomassie blue staining. (F) Concentration dependency of proteasome inhibition by SylA. Leaf extracts were incubated with various SylA concentrations and then labeled with MVB072. Proteins were analyzed on a protein gel using fluorescence scanning and Coomassie blue staining.