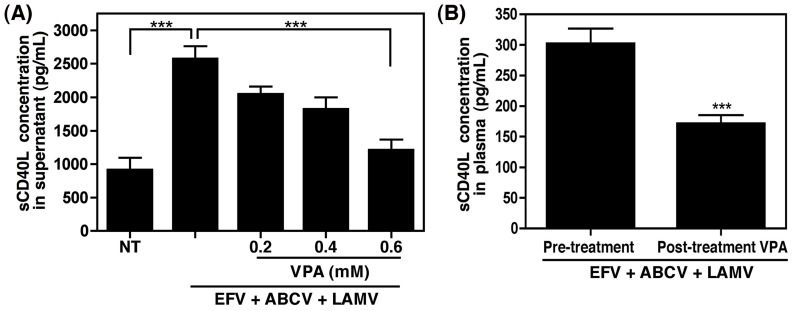
Figure 4. VPA inhibits EFV-induced sCD40L release from platelets both in vitro and in HIV infected individuals.
(A) Platelets isolated from healthy donors were treated with 5 µM EFV in the presence of NRTIs abacavir and lamivudine (ABCV and LAMV, respectively), and increasing amounts of VPA. The highest dose of VPA, which is equivalent to that measured in patients receiving the standard dose, significantly inhibited the EFV-induced release of sCD40L. Values were compared via one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test for multiple comparisons, which indicated statistical significance as ***p<0.001. (B) Plasma sCD40L levels were analyzed in HIV infected individuals receiving combination antiretroviral therapy including EFV (n = 11) prior to initiation of VPA therapy and after 7 days of VPA treatment (250 mg twice a day orally). VPA treatment significantly reduced the amount of sCD40L found in the plasma of these patients. Values were compared using a paired t-test with statistical significance indicated as ***p<0.001.