Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of primates, and status of the captured endogenous retrovirus envelope genes with placental expression.
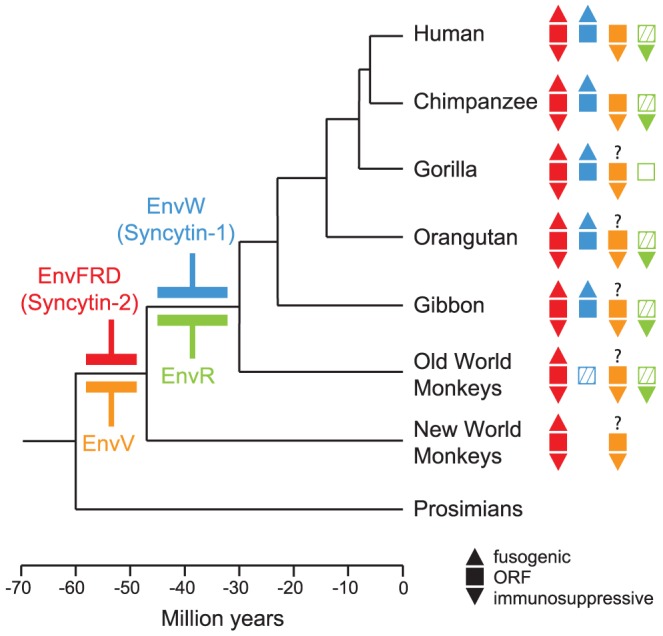
The date of insertion of the indicated retroviral envelope genes into the genome of primate ancestors is indicated for the syncytin genes (i.e. the EnvFRD- and EnvW-encoding genes, in red [8] and blue [6], respectively, and for the EnvV- and EnvR-encoding genes, in orange [27] and green [26], respectively). Their presence in the various primate lineages is indicated with filled squares when the gene still possesses a full-length ORF, with hatched squares when the coding sequence is prematurely interrupted, and an empty square when the gene is no longer present. In addition, fusogenic activities (as determined by ex vivo cell-cell fusion assays in ref [5], [8]) are schematized with an upper triangle when present, and immunosuppressive activities (as assayed in ref [19]) with lower triangles. Branch length is proportional to time (in million years).
